こんにちは、レシピサービス開発部の@miichan_ochaです。普段はiOS版クックパッドアプリの開発をしています。
クックパッドアプリでは開発した機能の評価を行うために、画面のPVログや画面内の各コンテンツの表示・タップログなどの様々な行動ログを送っています。
今回は、SwiftUIで新たに作った画面内の各コンテンツの表示ログを送る仕組み(ShowContentLog)についてご紹介します。この仕組みは昨年7月にリリースされたiOS版クックパッドアプリ「のせる」タブ開発時に作られたもので、現在約半年ほど運用しています。
ログの要件
レシピサービス開発部では、iOS版クックパッドアプリの画面内の各コンテンツの表示ログを以下の要件で取っています。
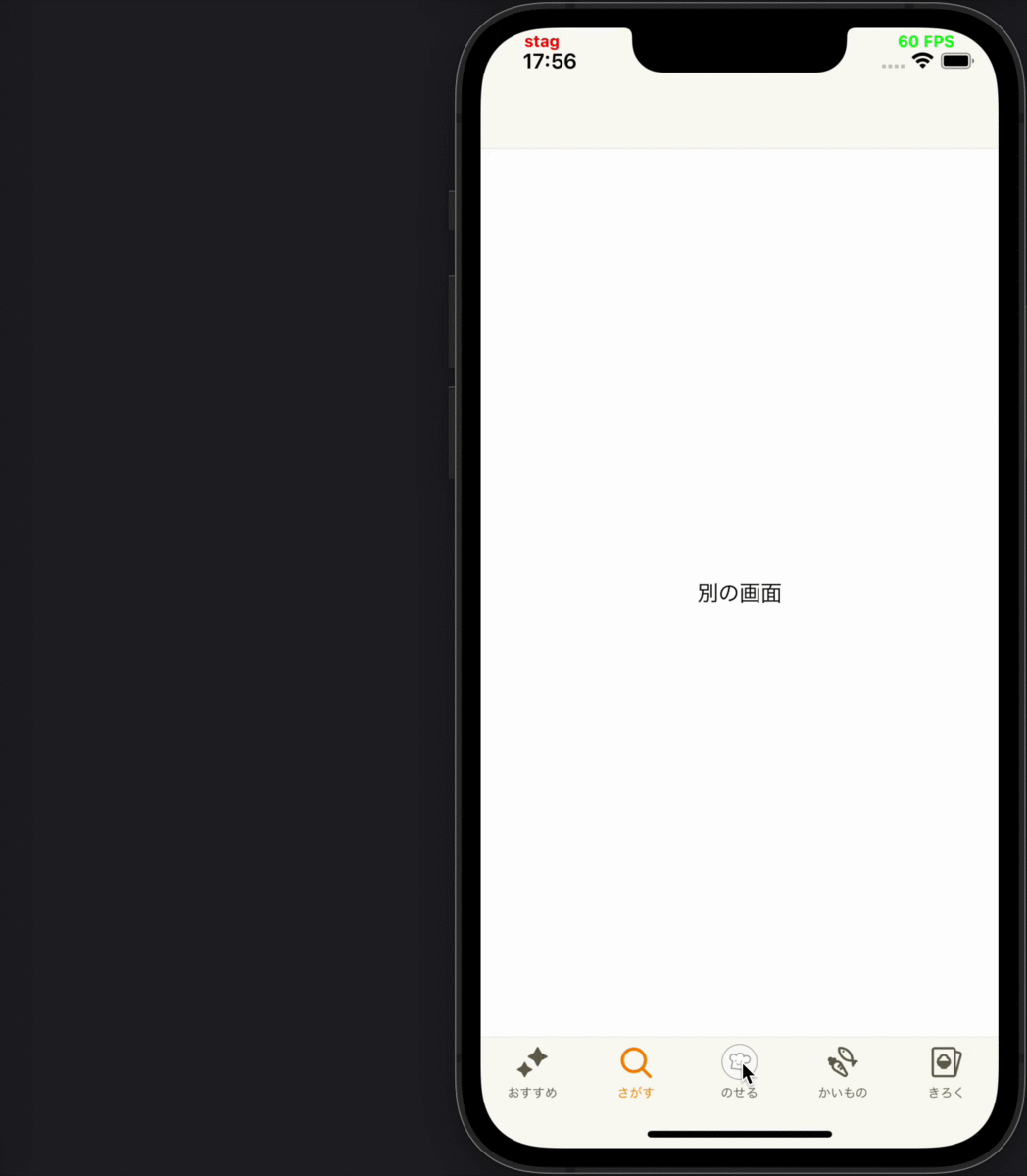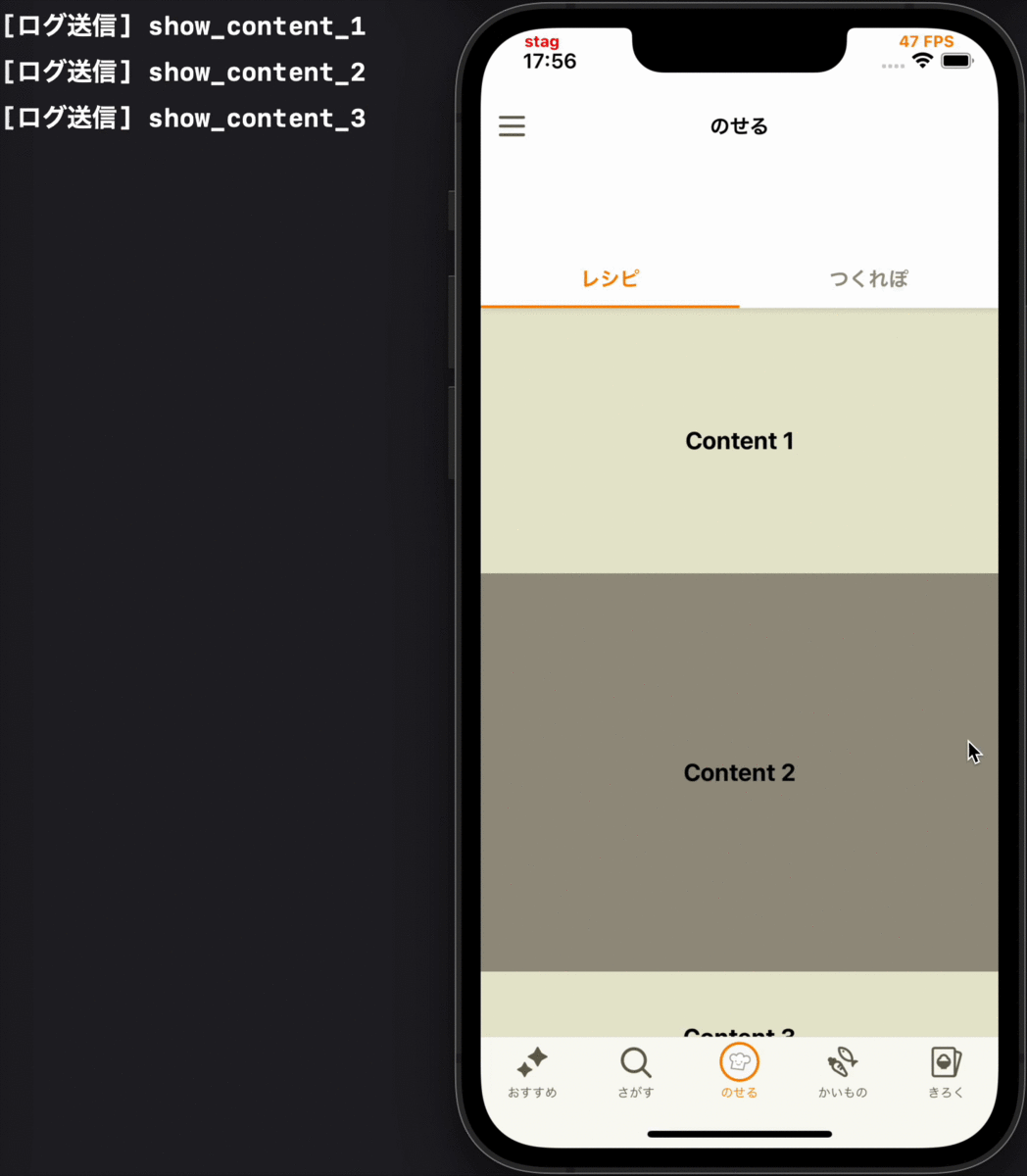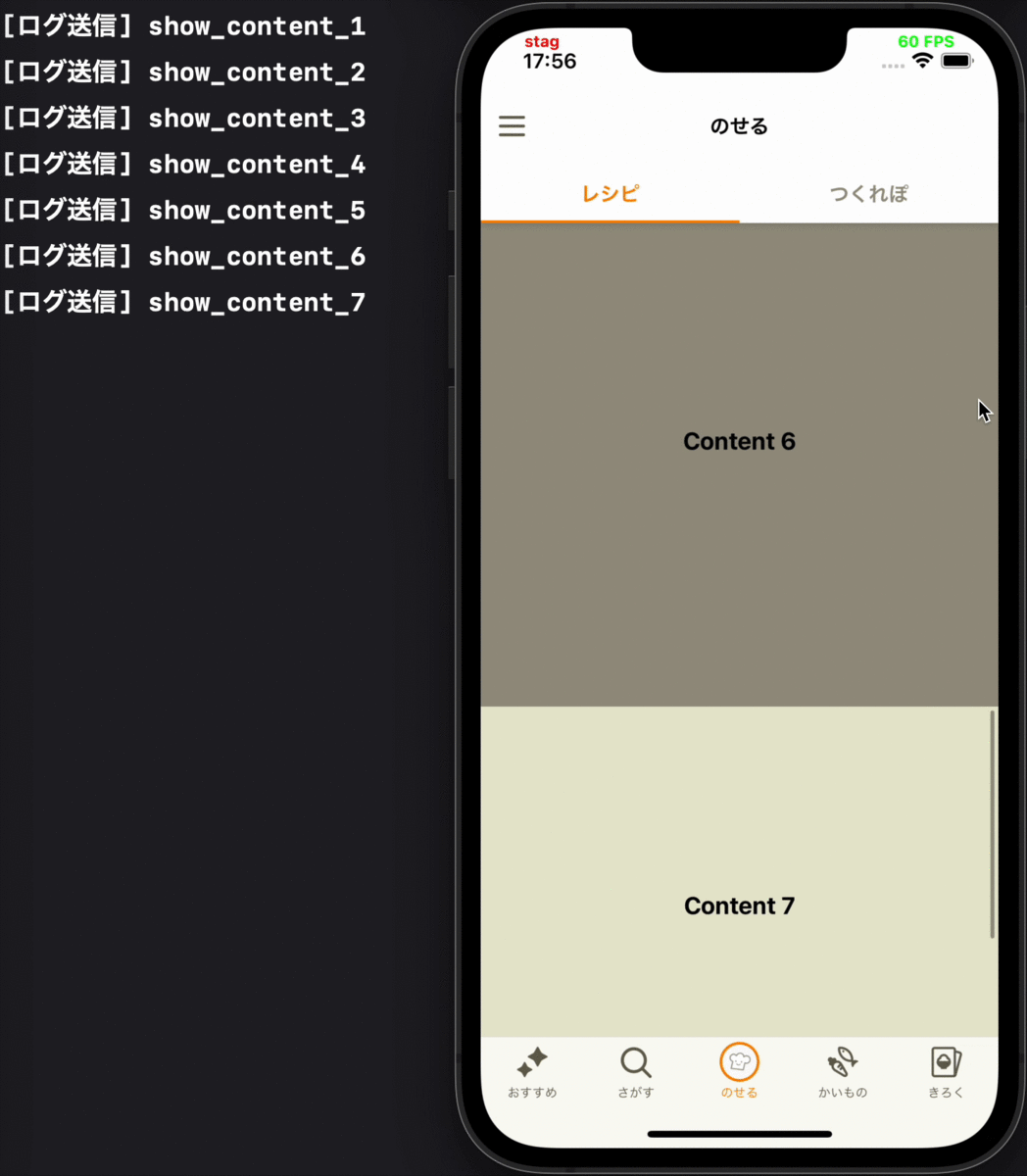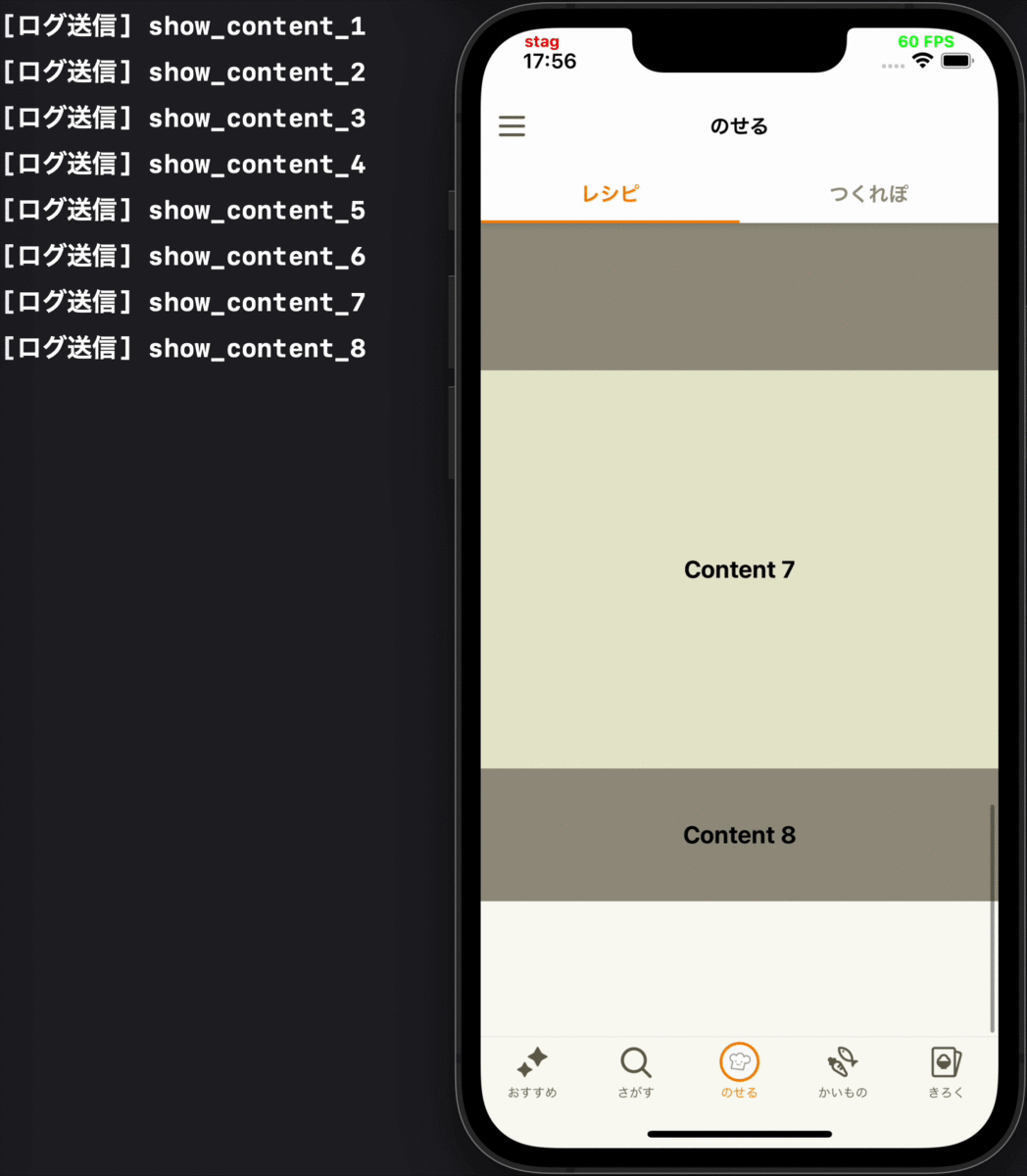
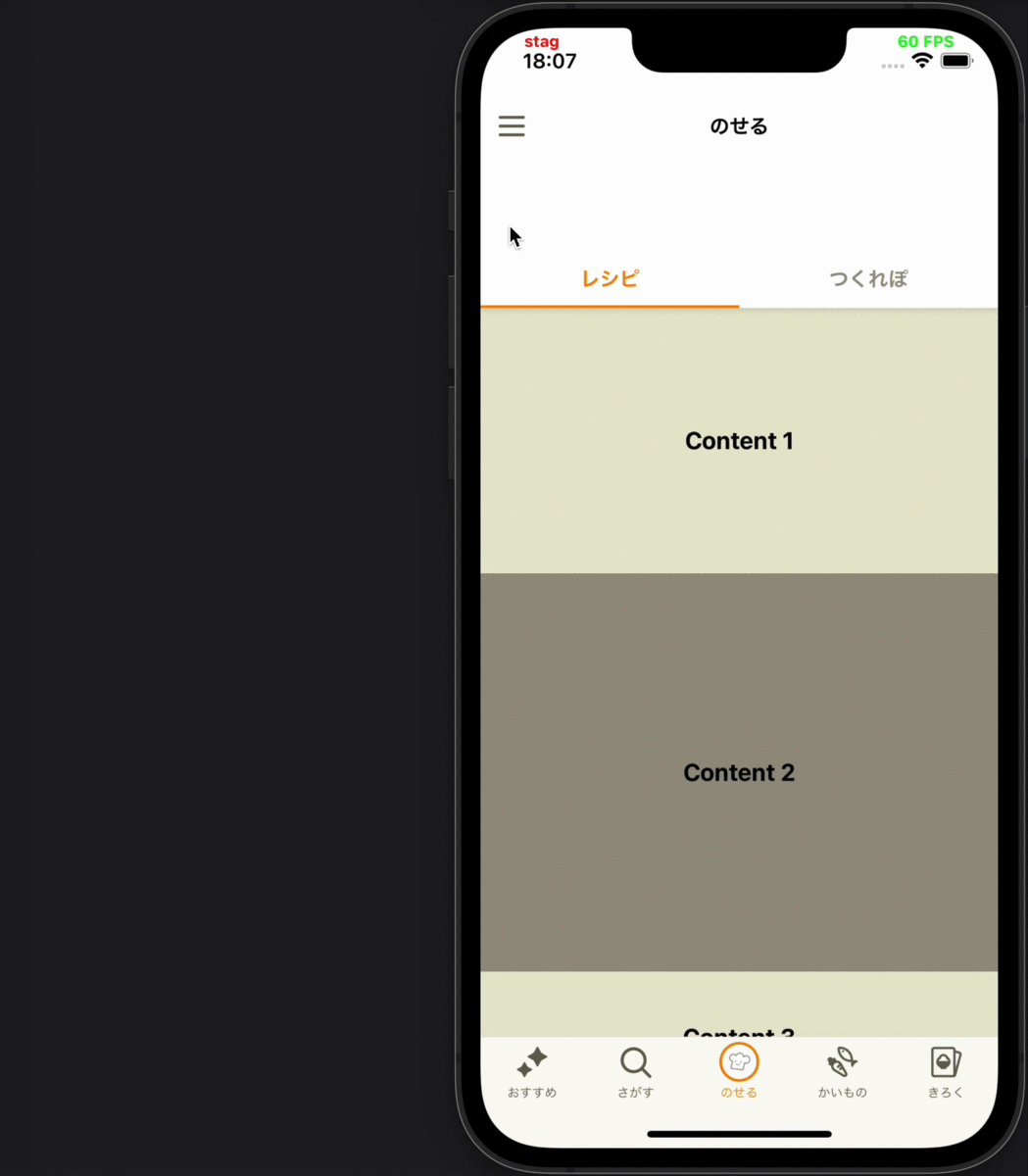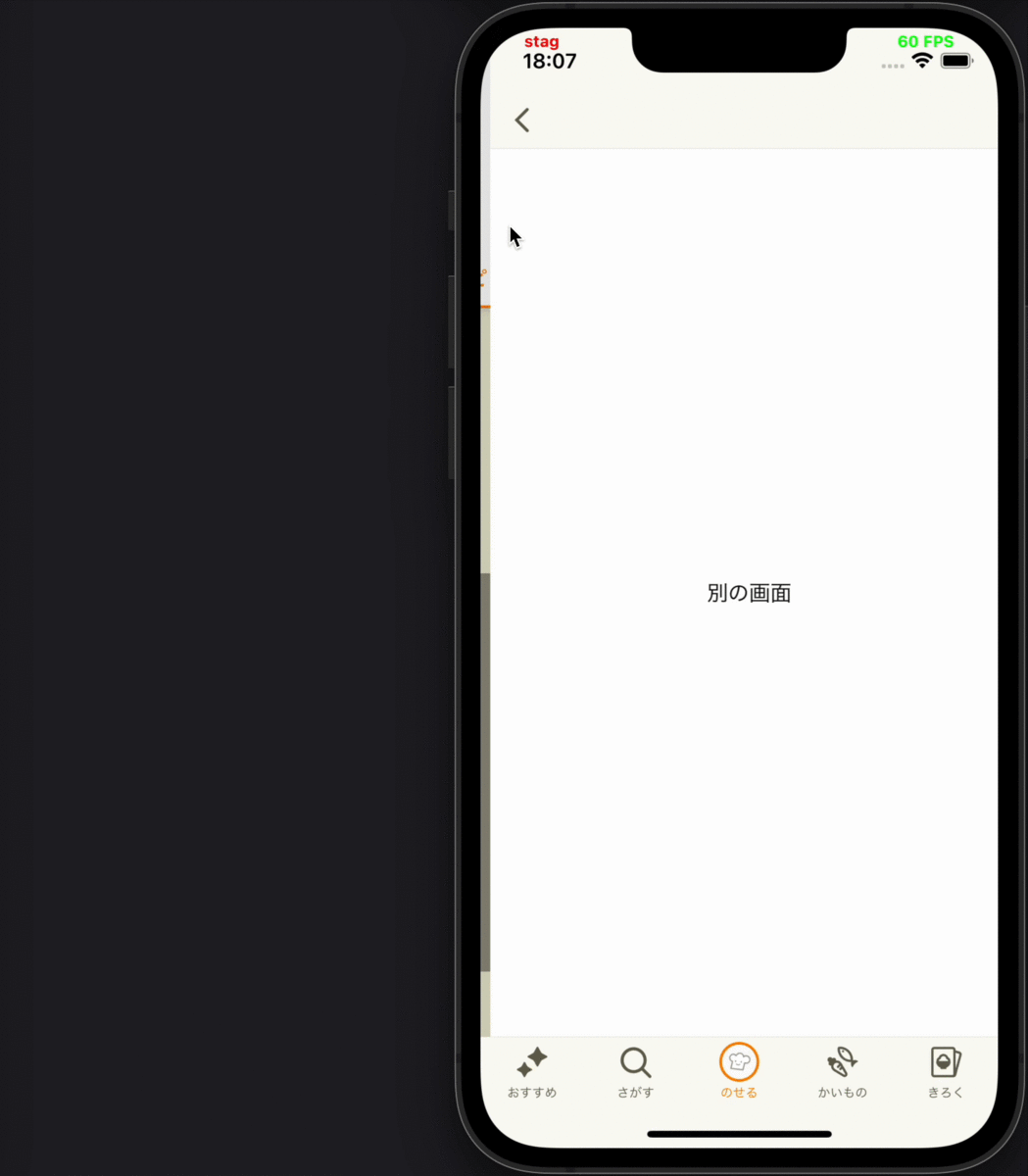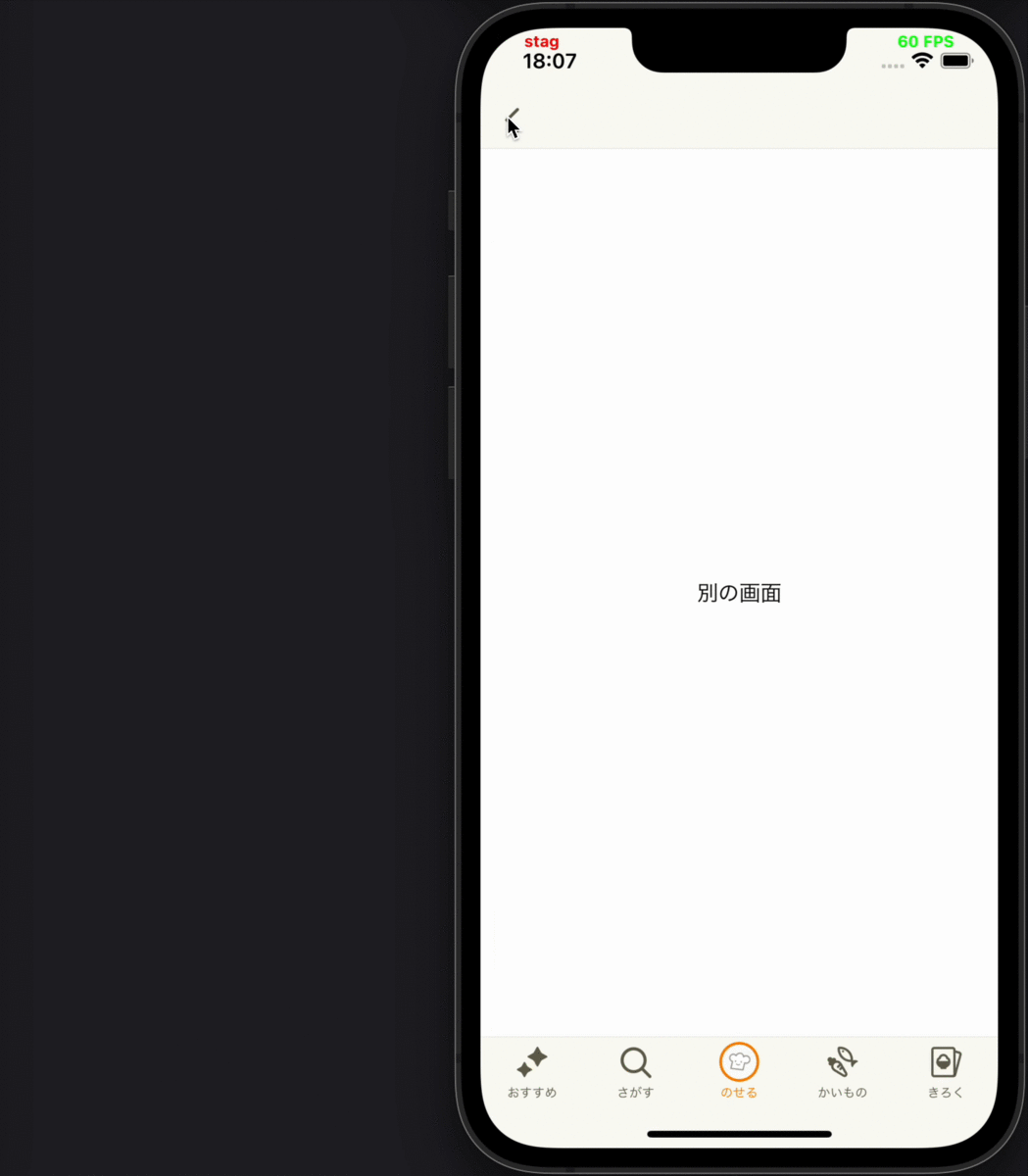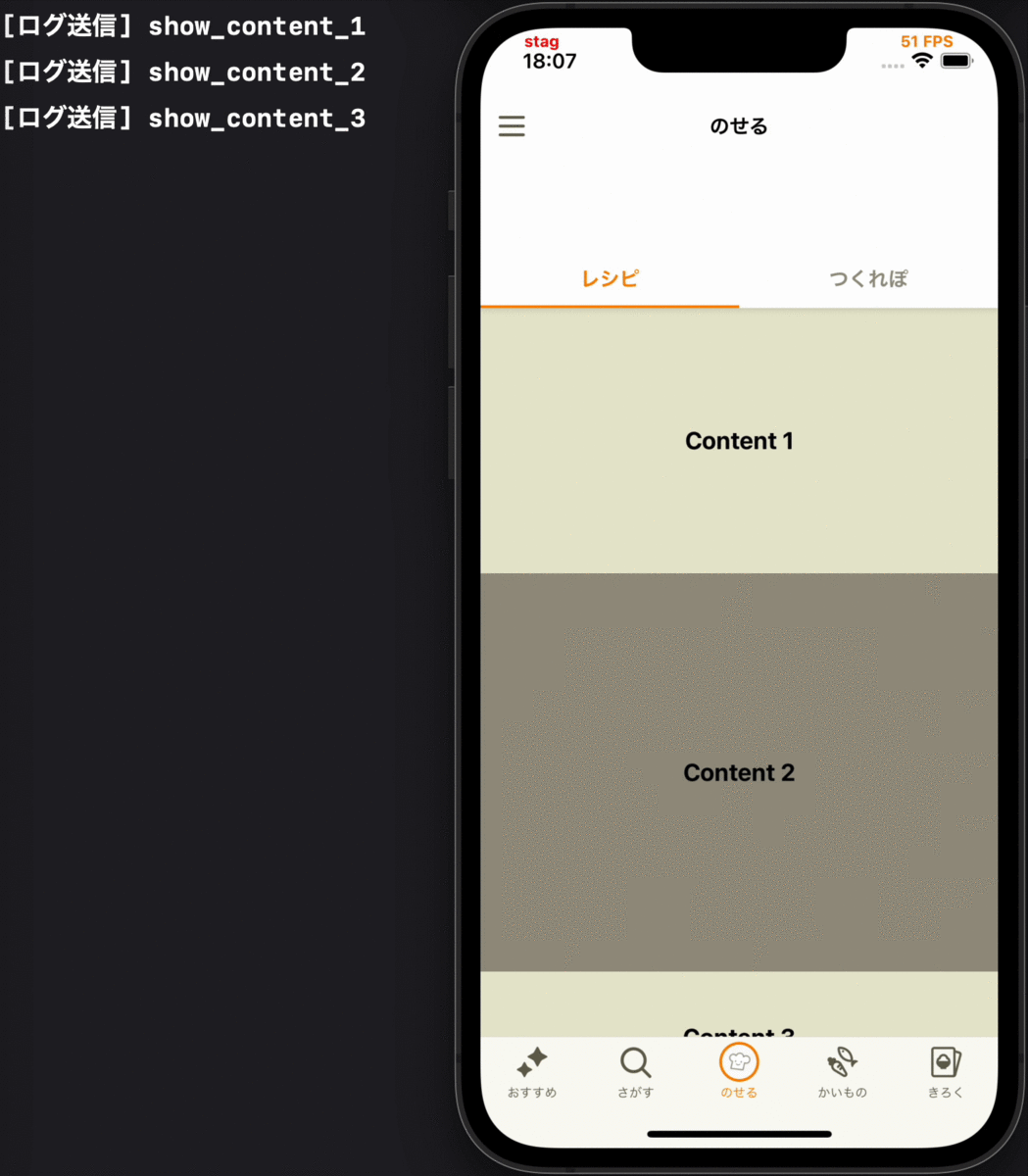
- コンテンツが初めて画面に表示される時に、そのコンテンツの表示ログを送る
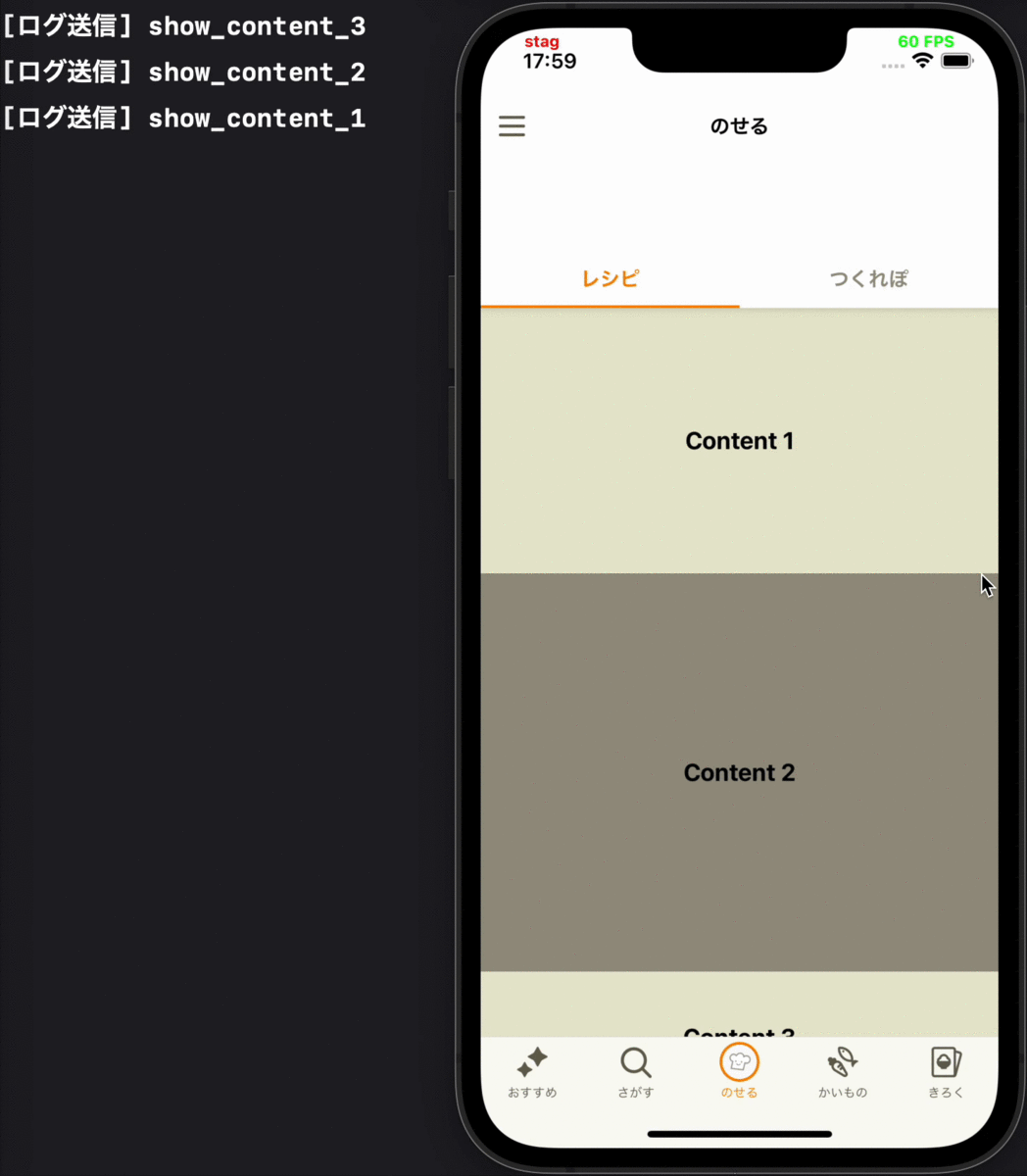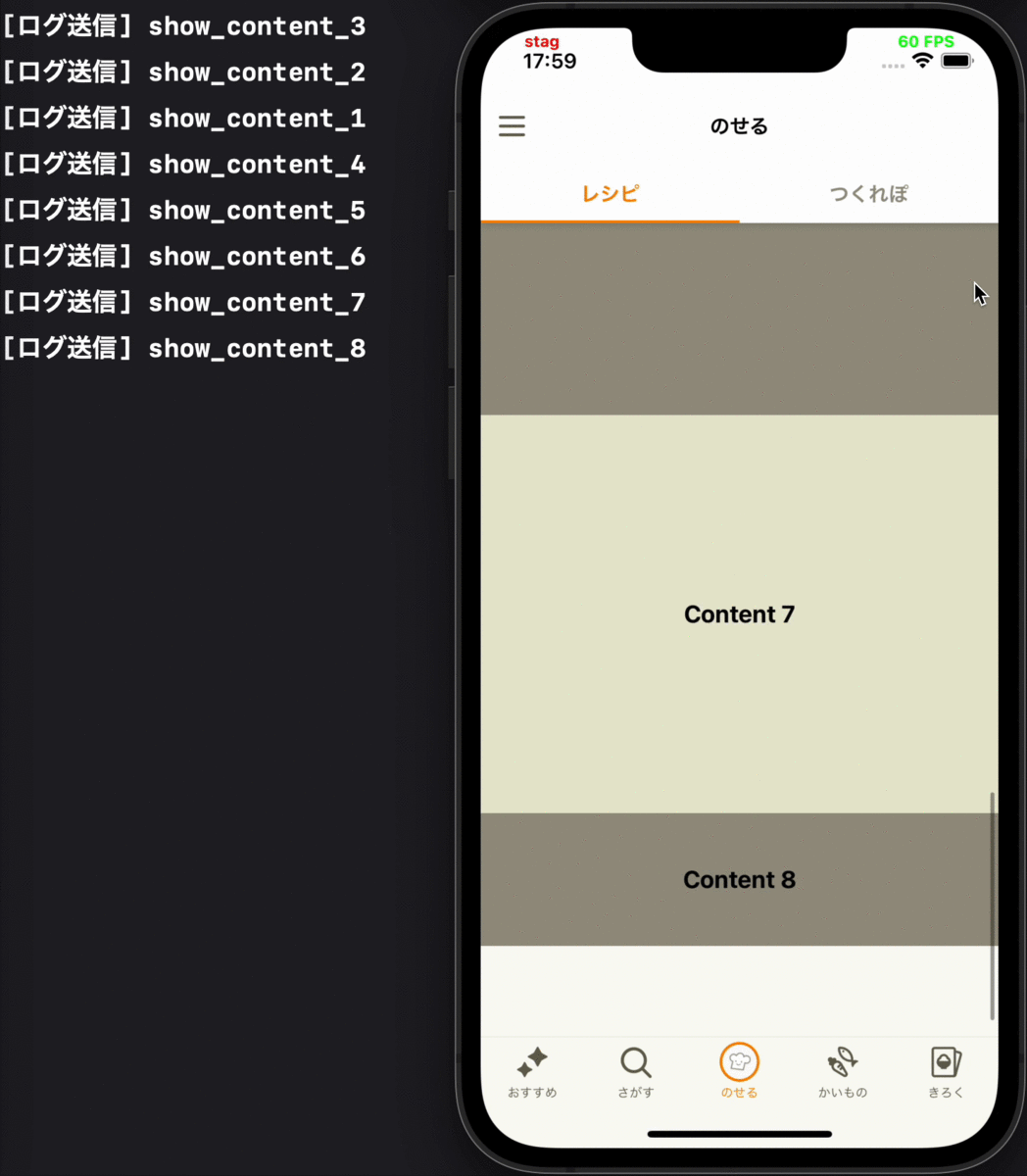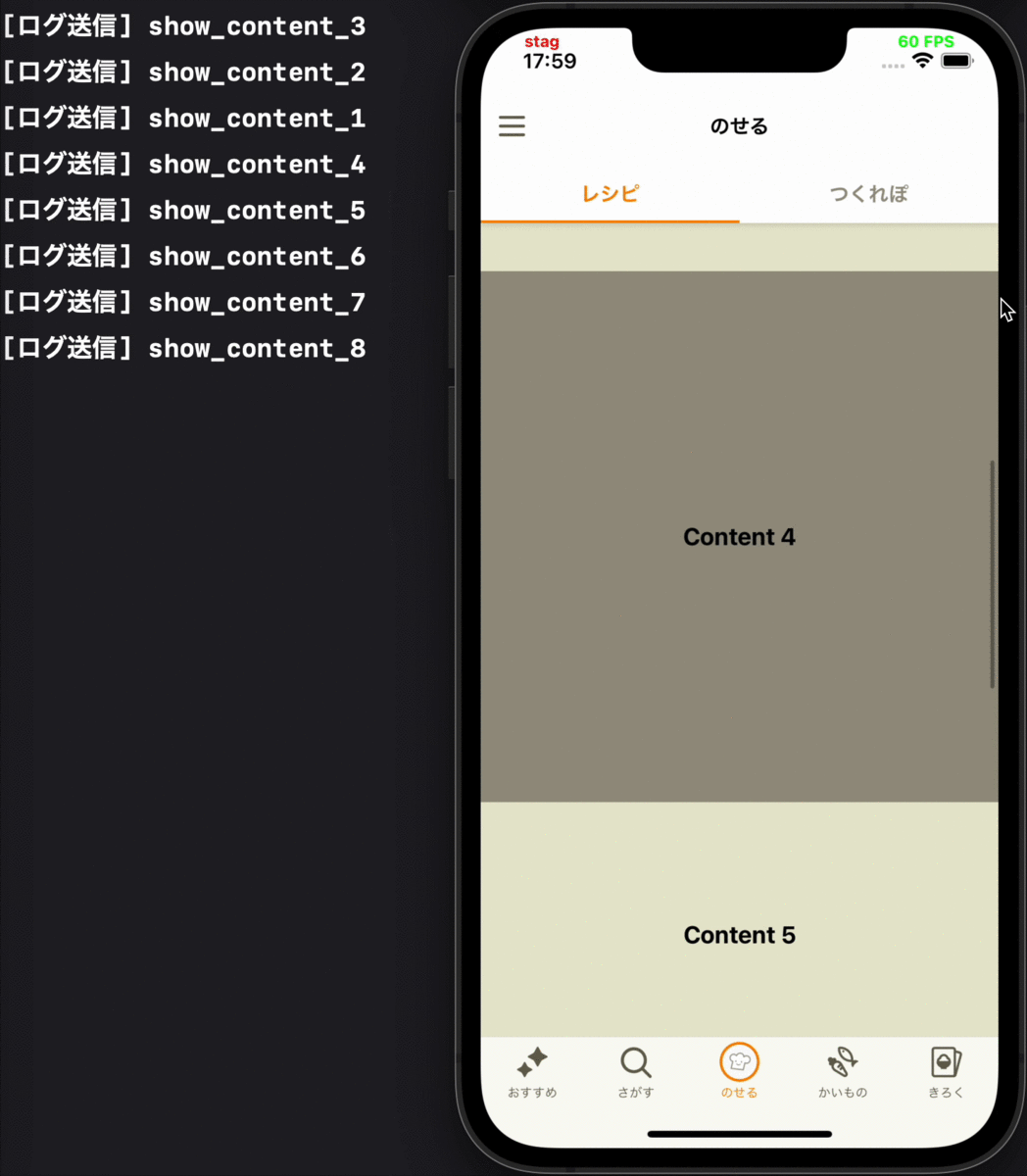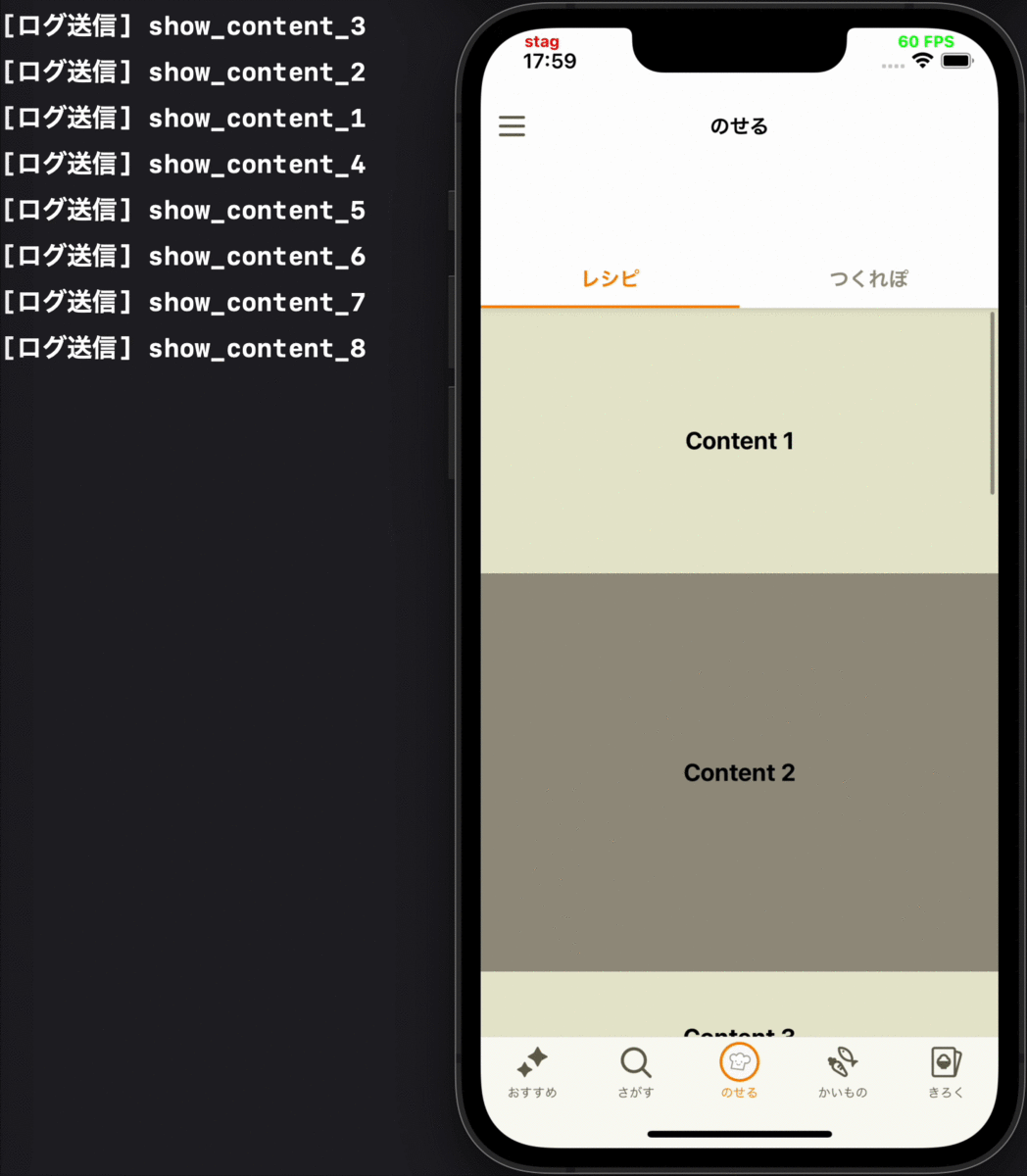
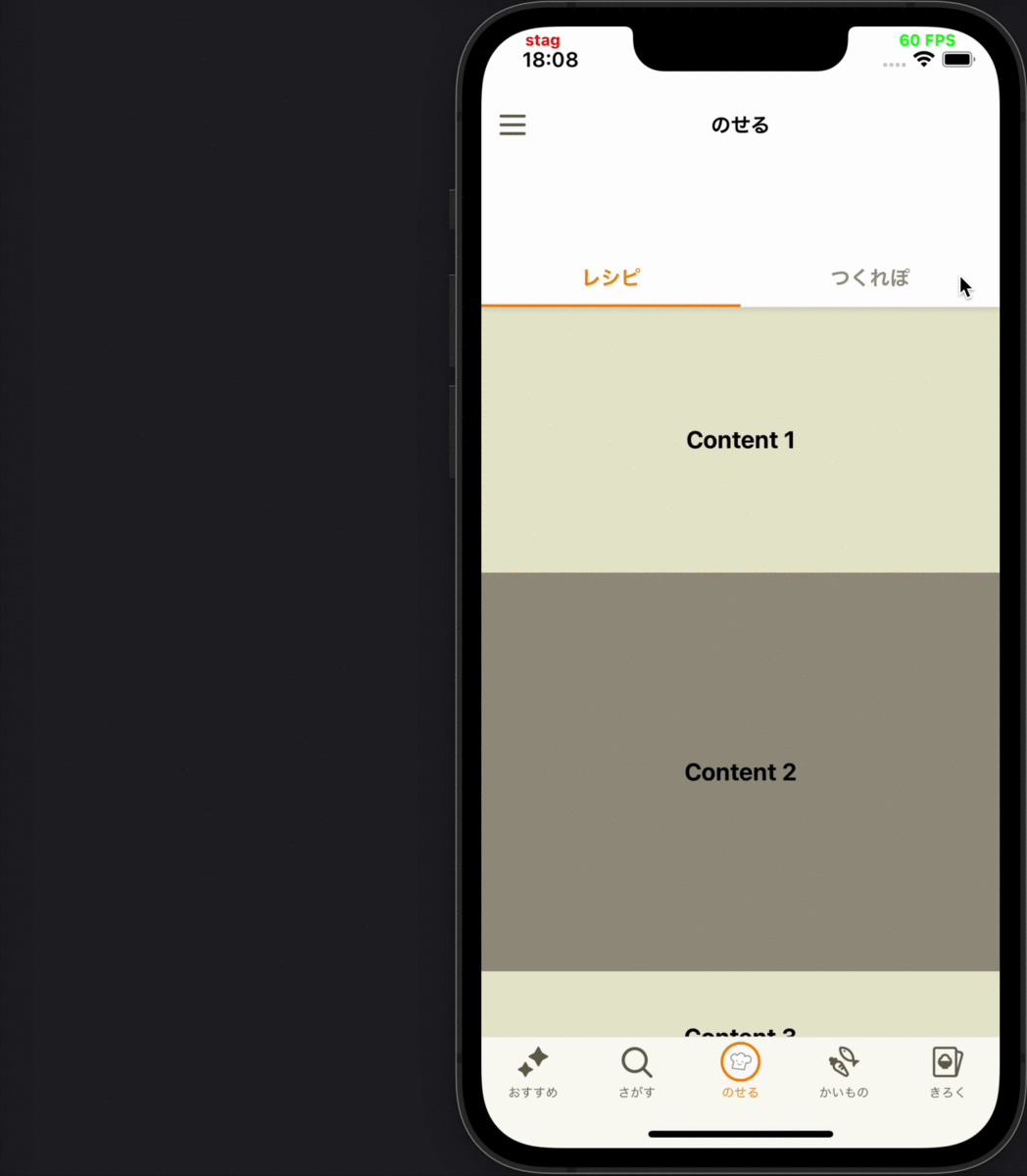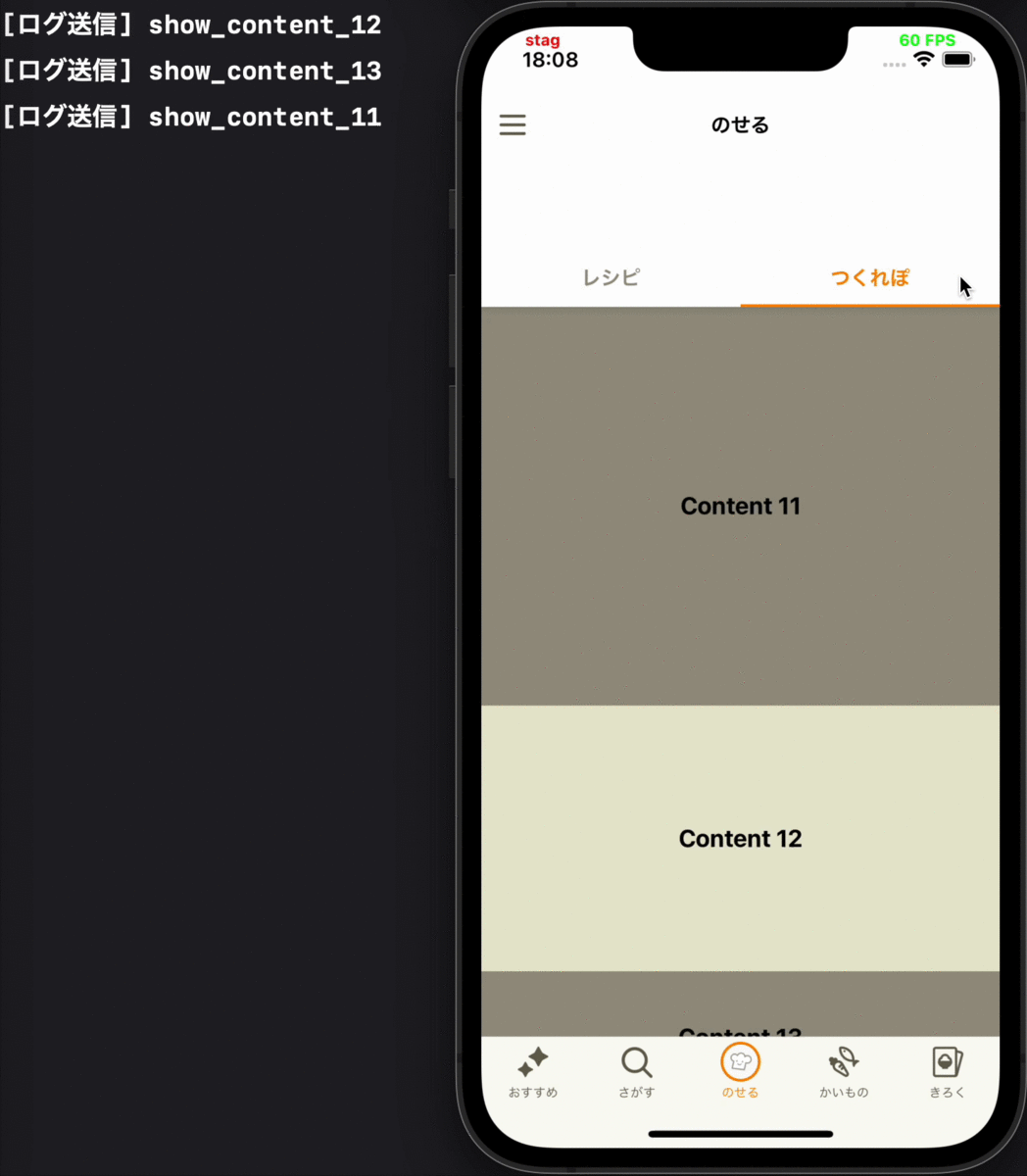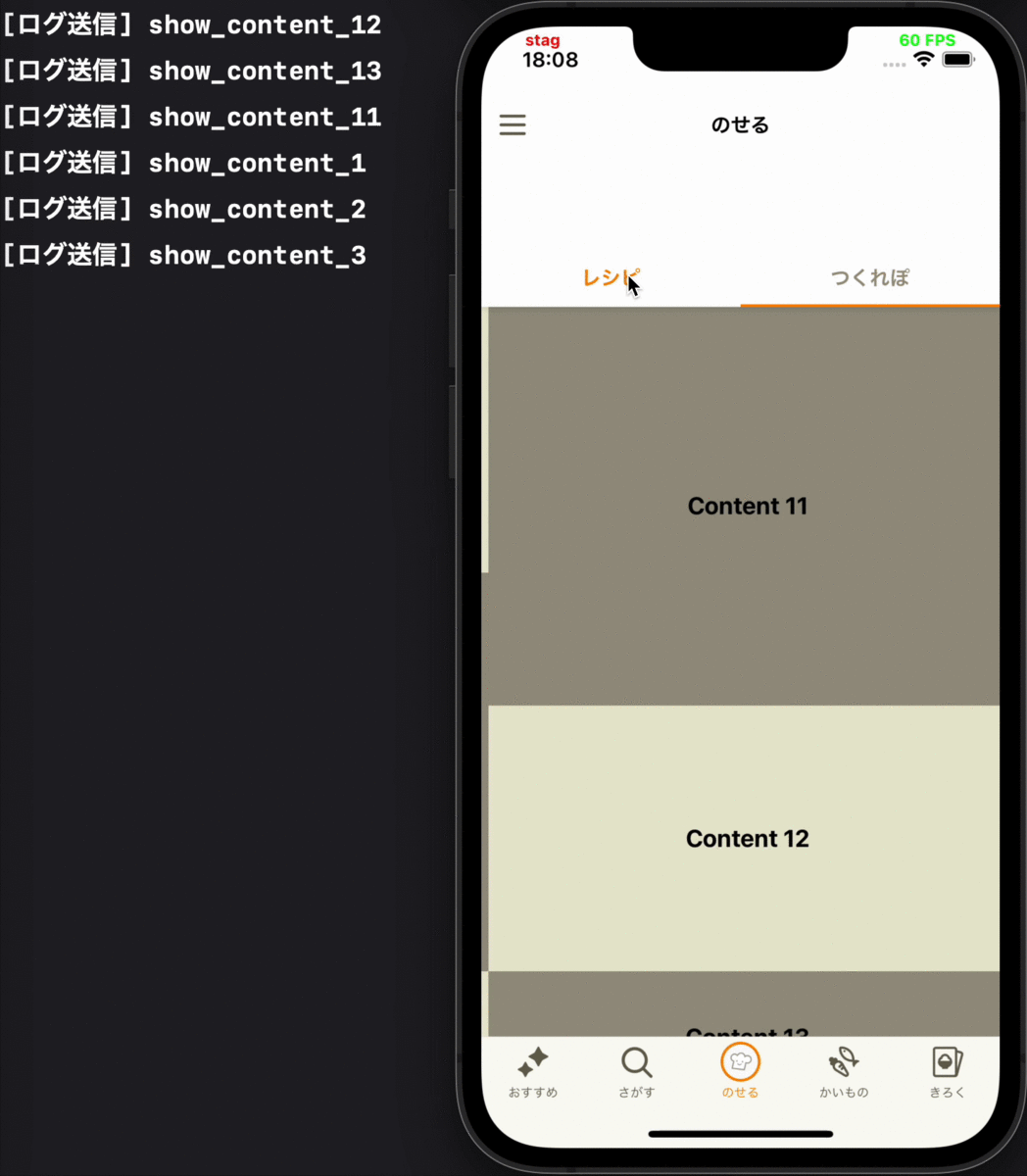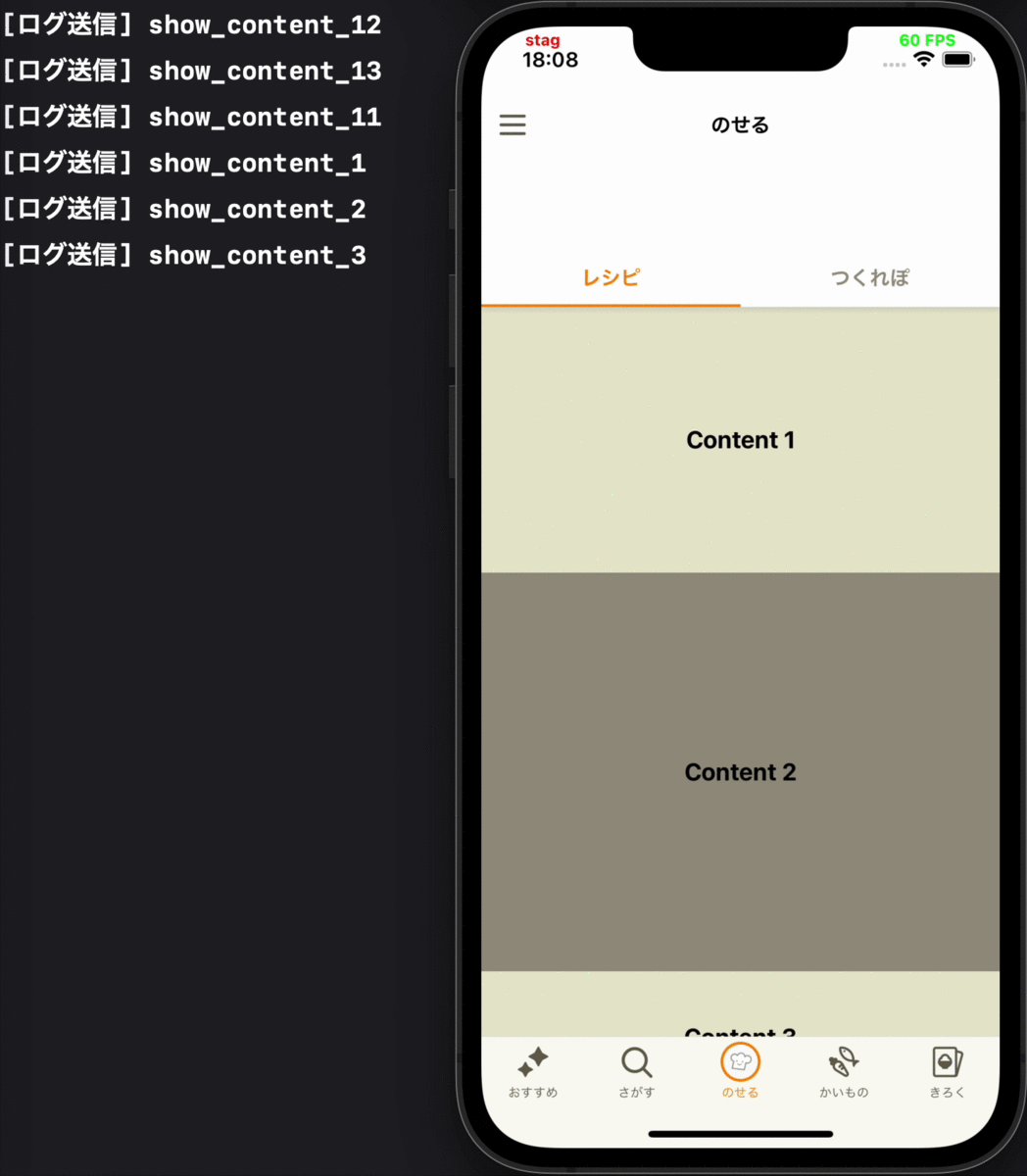
- 画面のスクロールによって、コンテンツが一度画面外に出てから再度画面内に表示された時には、そのコンテンツの表示ログは送らない
- 一定時間経過後の画面自動更新やPull to Refreshによる画面更新を行った時は、更新後の画面に表示されているコンテンツの表示ログを送る
- 別画面にプッシュ遷移した後、遷移先から戻ってきて画面が再度表示された時に、その画面に表示されているコンテンツの表示ログを送る
- タブの切り替えによって画面が再度表示された時に、その画面に表示されているコンテンツの表示ログを送る
- アプリがバックグラウンドからフォアグラウンドに復帰した時に、復帰時の画面に表示されているコンテンツの表示ログを送る
各要件に対応するデモ動画
| 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
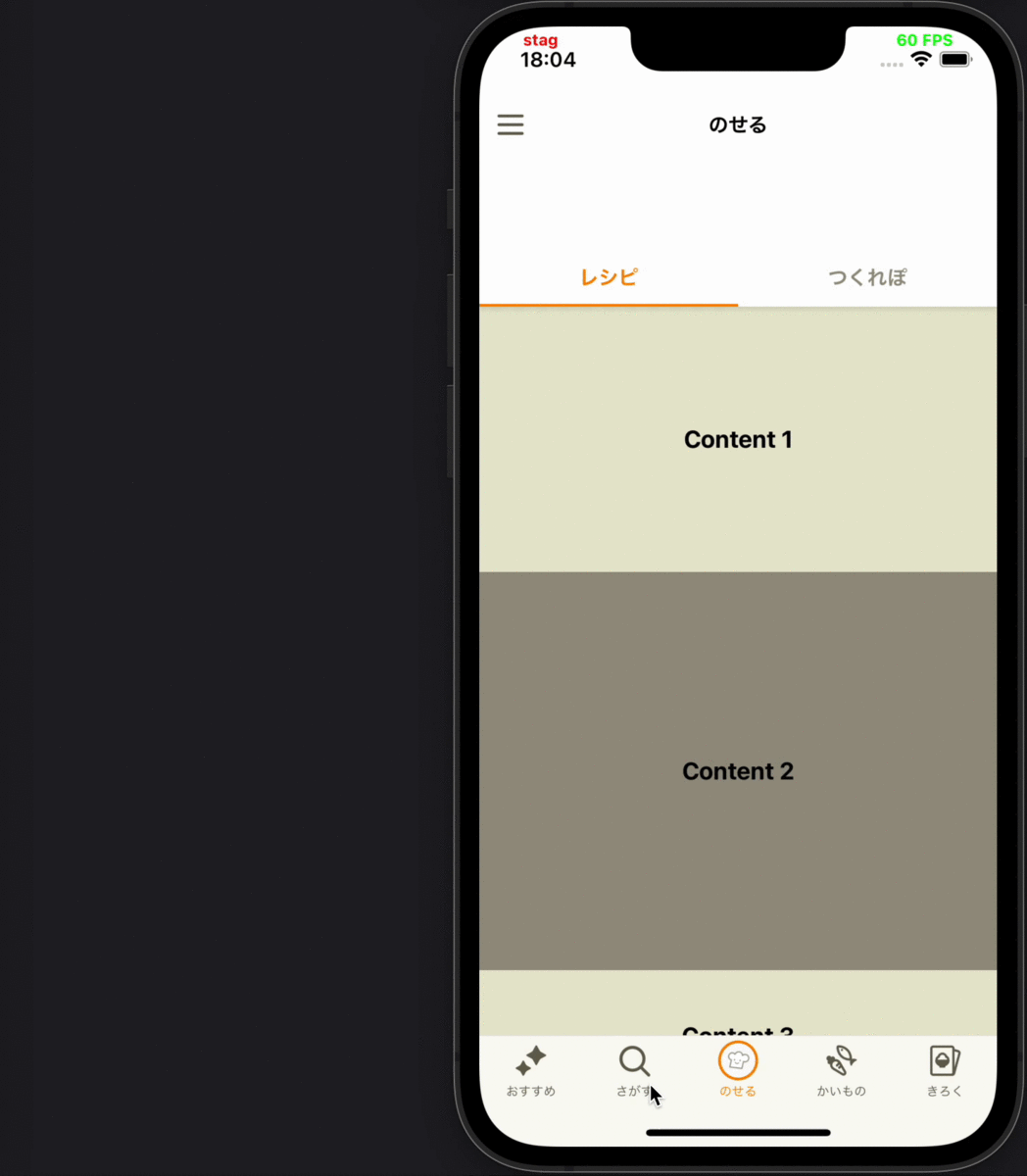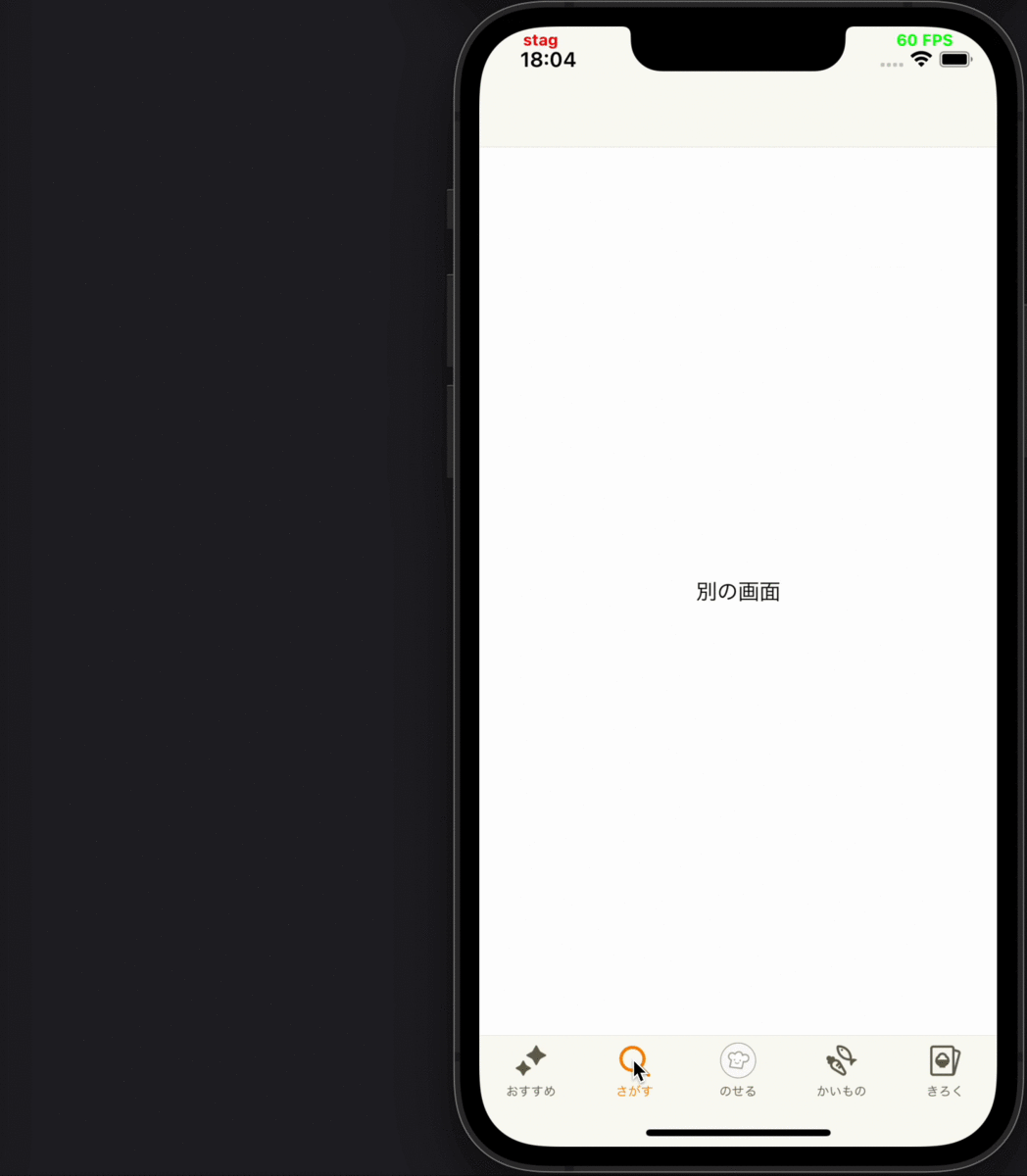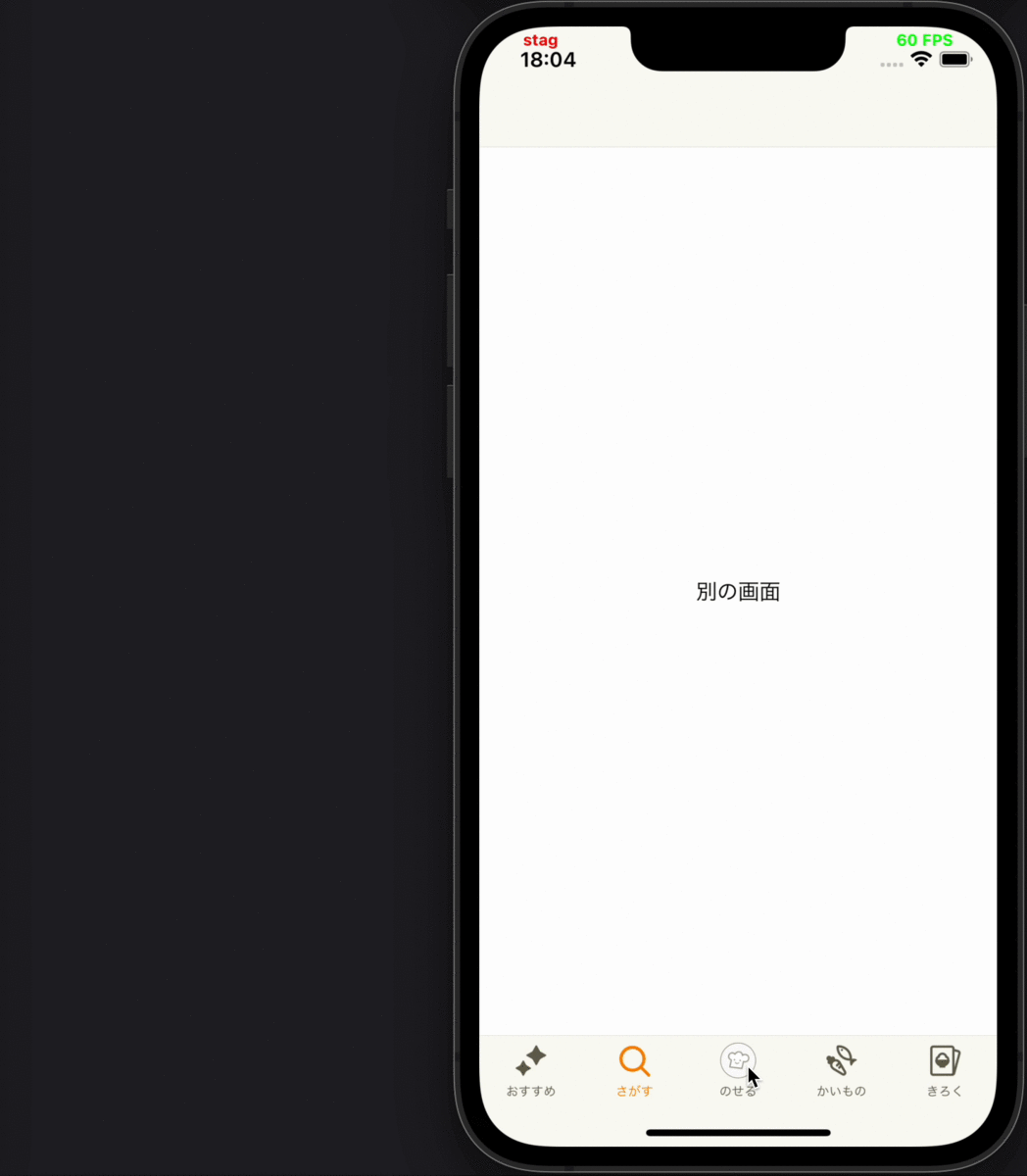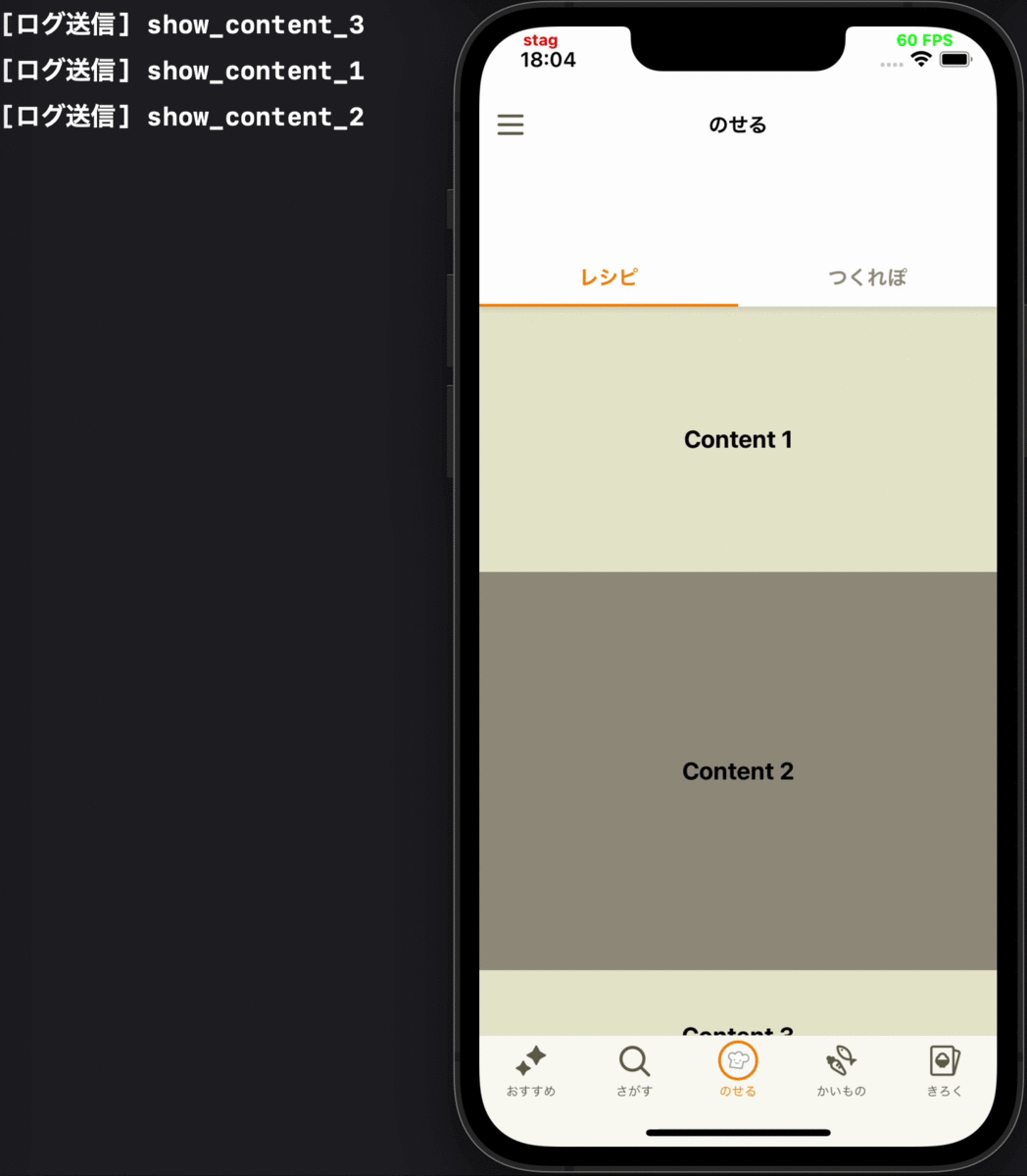 |
| 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
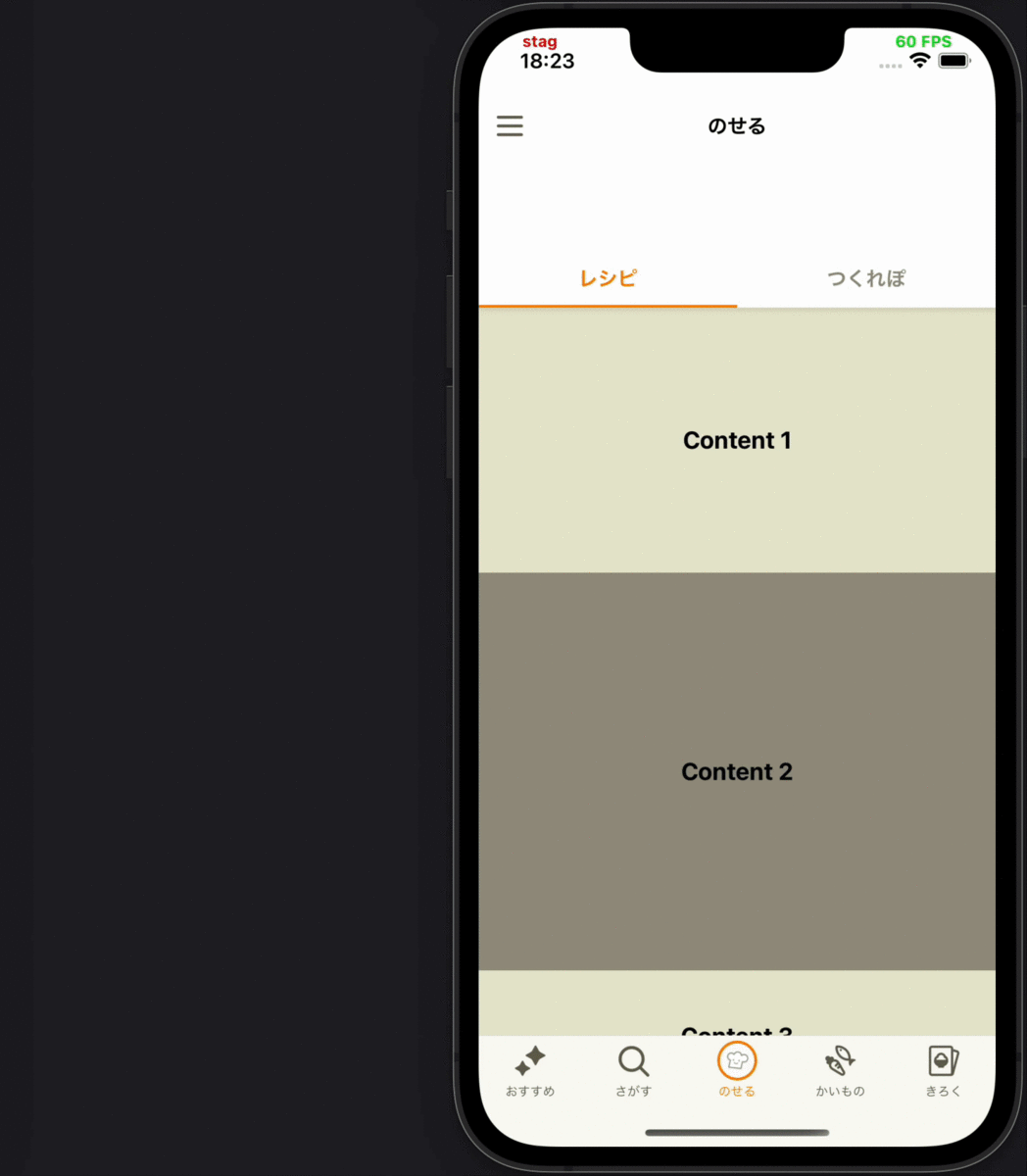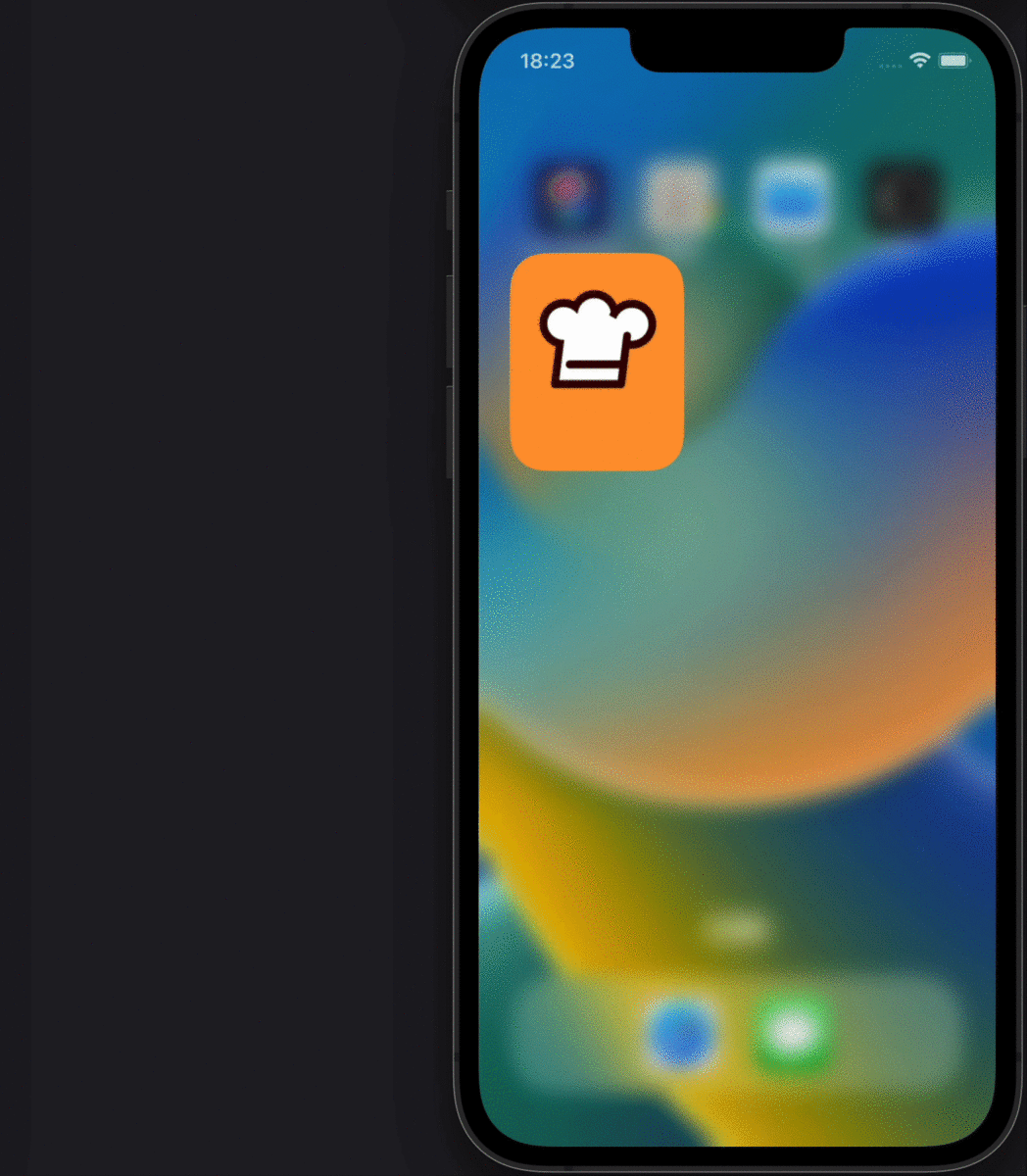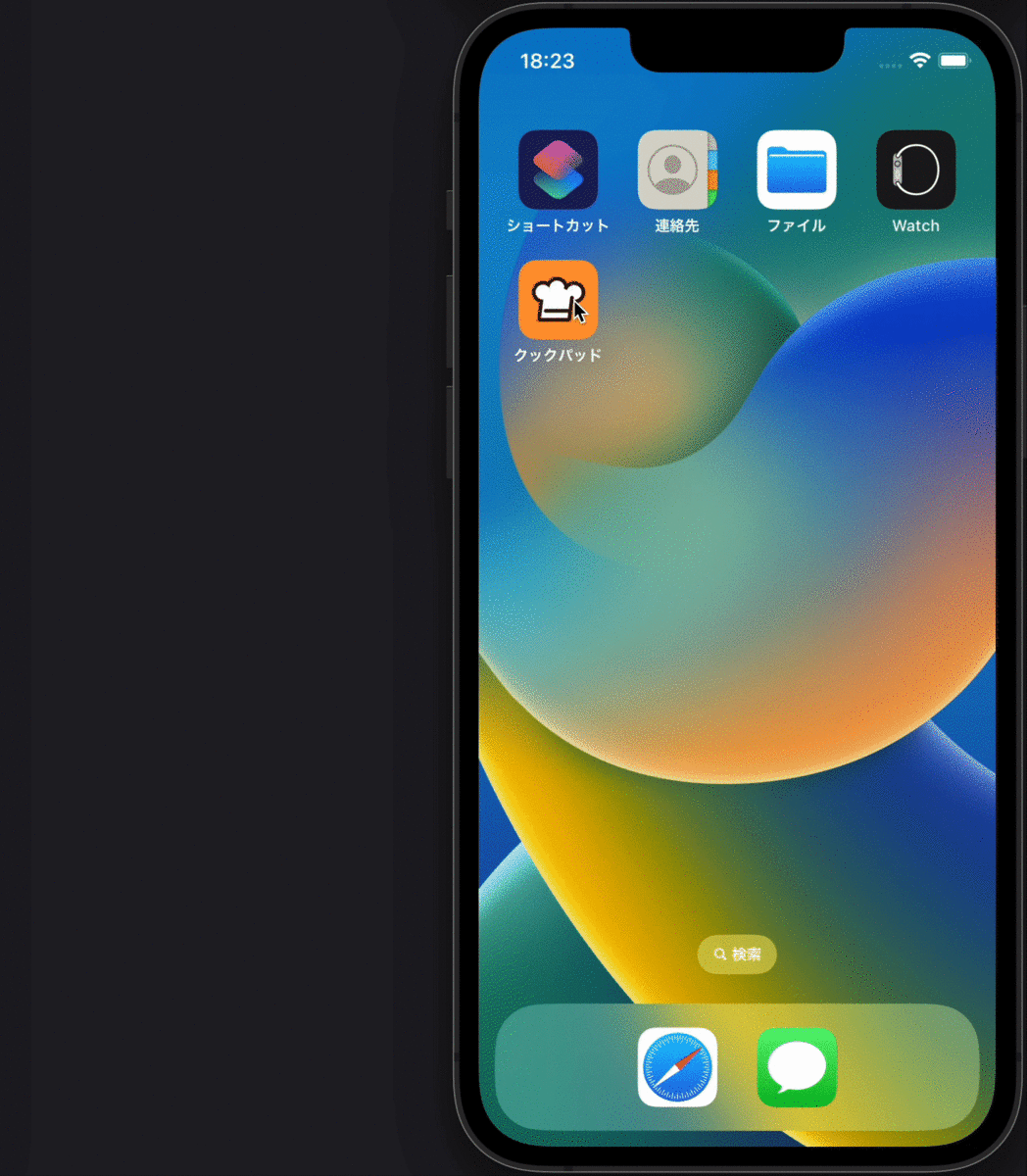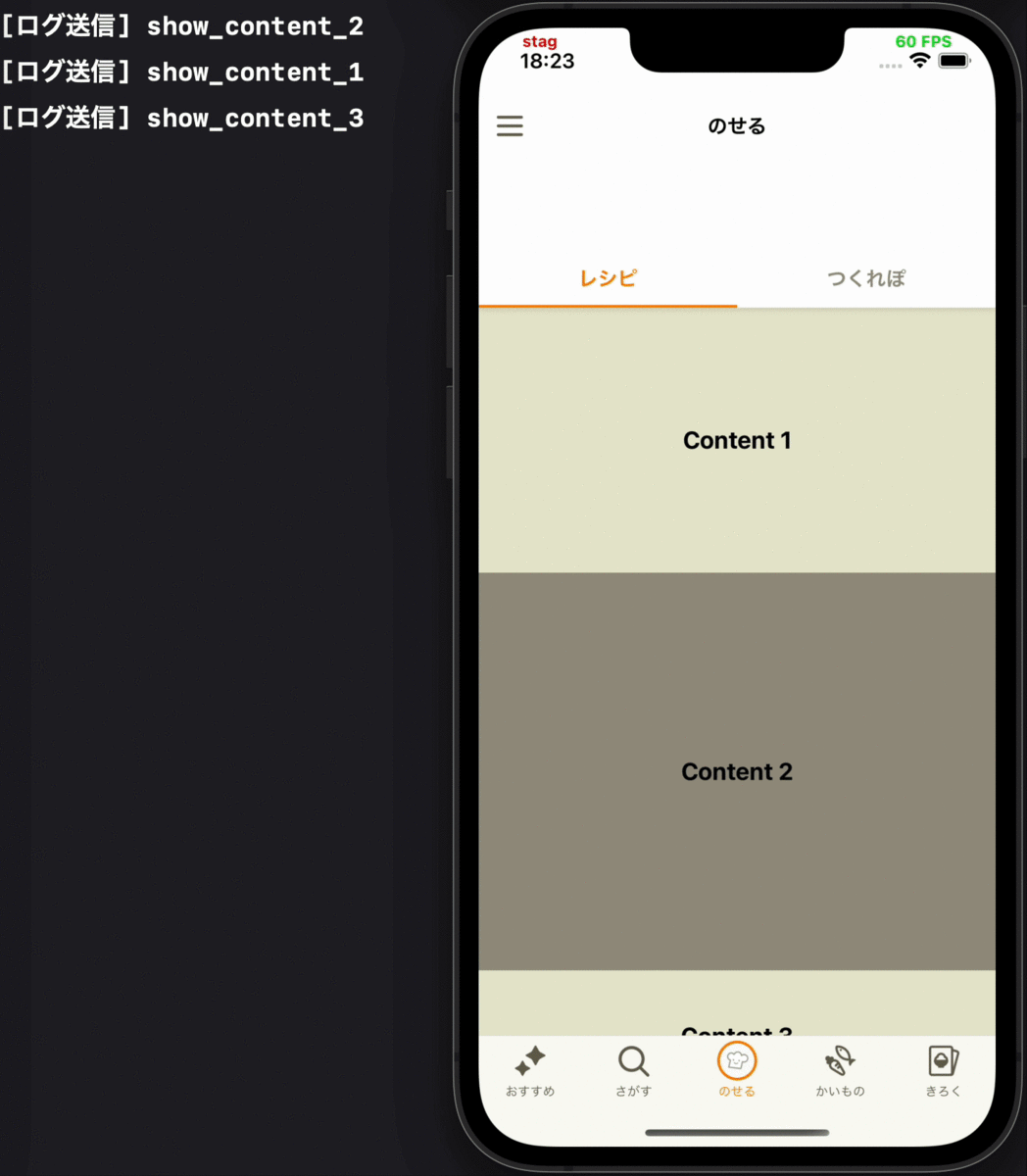 |
なお、ここでいう各コンテンツとは「表示・タップ回数を計測したいViewのまとまり」のことを指しており、ある画面では画面内のセクション単位であったり、別の画面ではバナー・カルーセルなどViewのコンポーネント単位であったりと、その粒度は画面によって様々です。
UIKitで作られた画面では、ViewController内で表示された各コンテンツのIDを管理するSetをpropertyとして保持し、UICollectionViewで作られた画面であればUICollectionViewDelegateのcollectionView(_:willDisplay:forItemAt:)をトリガーにログを送信することでこの要件を実現していました。
仕組みが必要になった背景
きっかけは前述の通り、レシピサービス開発部で「のせる」タブの画面をSwiftUIで作ったことです。
「のせる」タブでは上記の仕様で各コンテンツの表示ログを送る要件があったため、SwiftUIの画面でも各コンテンツの表示ログを送る必要が出てきました。加えて、UIKitでは画面ごとに都度表示ログを送る実装をしていましたが、SwiftUIでは仕組み化して簡単に送れるようにしたいという動機から、今回の仕組みが生まれました。
動作する環境について
今回の仕組みはiOS版クックパッドアプリ上で使用されており、以下の条件・環境で動作しています。
iOS版クックパッドアプリで採用しているVIPERアーキテクチャに適合したまま、View層のみでSwiftUIを使っている
表示ログを送る各コンテンツは、
LazyVStackやListなど、遅延ロードを行うViewの中に配置されている必要がある- 各コンテンツが表示されたかどうかは onAppear/onDisappear で判定しているため
Markdownで書かれたログ定義から自動生成された行動ログ(以下「自動生成行動ログ」と呼びます)を送る前提で設計されている(追加で別のログを送ることも可能)
- この自動生成の仕組みについては https://techlife.cookpad.com/entry/2020/11/05/110000 に詳しい解説があります
iOS Deployment Targetが 14.0 の時代に開発された
- iOS13での動作は未検証となっています
ShowContentLogの使い方
まずは、仕組みの使い方について簡単に説明します。
*説明のためコードを簡略化しています。完成版のコードに関しては「完成版のコード」の章をご覧ください。
最初に、UIHostingControllerを保持しているViewController内でShowContentLogControllerというクラスのインスタンスを作成します。
// ViewController private lazy var showContentLogController = ShowContentLogController(screenViewController: self)
次に、表示ログを送る各コンテンツを内包しているView(以下「大元のView」と呼びます)に ShowContentLogRootModifierというViewModiferを付与します。これにより、このViewModiferを付与したViewが表示されている時にだけ、各コンテンツのログが送られるようになります。
シンプルな画面ではUIHostingControllerの引数に渡すrootViewのViewにShowContentLogRootModifierを付与すれば良いですが、タブがある画面においては、各タブの中身のViewごとに付与します(各タブで表示状態が異なるため)。
ShowContentLogRootModifierの引数controllerには、先程作成したShowContentLogControllerのインスタンスを渡します。各タブの中身のViewごとにShowContentLogRootModifierを付与した場合は、タブの数だけShowContentLogControllerのインスタンスを作成し、タブごとに別々のインスタンスを渡してください。
*このViewModiferに対応するshowContentLogRootというメソッドをSwiftUI.Viewにextensionとして定義しています。
// ViewController override func viewDidLoad() { super.viewDidLoad() let rootView = HogeView(delegate: self, dataSource: dataSource) .showContentLogRoot(controller: showContentLogController) let hostingVC = UIHostingController(rootView: rootView) ... }
最後に、表示ログを送りたい各コンテンツのViewそれぞれにPostShowContentLogModifierというViewModiferを付与します。引数eventにはLogCategory protocolに準拠したログイベントを渡します(「自動生成行動ログ」の全てのログイベントはLogCategoryに準拠しています)。
RecipeView()
.postShowContentLog(SampleCategory.showRecipe(recipeId: recipe.id))
以上で、ログの要件通りに各コンテンツの表示ログを送ることができるようになります。
ShowContentLogの設計
次に、このShowContentLogの設計・内部実装について詳しく見ていきます。
*ここでもコードは適宜簡略化しています。簡略化されていないものは「完成版のコード」の章をご覧ください。
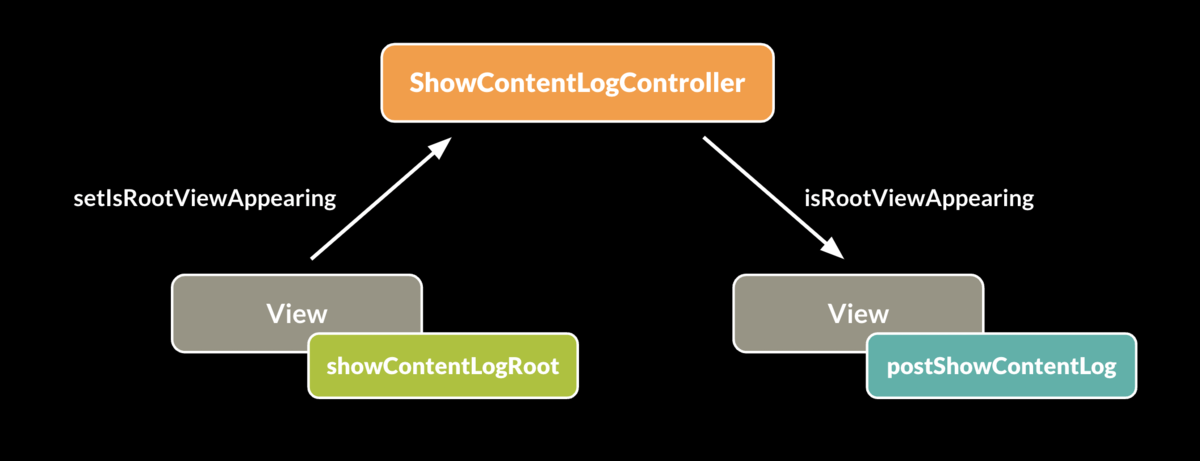
ShowContentLogController
ShowContentLogControllerは、表示ログを送る「大元のView」の表示状態を、子Viewである各コンテンツのViewに通知する役割を担うクラスです。isRootViewAppearingというPublisherを持ち、各コンテンツのViewはこれを監視することで「大元のView」の表示状態を知ることができます*1。
@MainActor final class ShowContentLogController { private let isRootViewAppearingSubject = CurrentValueSubject<Bool, Never>(false) lazy var isRootViewAppearing: AnyPublisher<Bool, Never> = isRootViewAppearingSubject .removeDuplicates() .eraseToAnyPublisher() func setIsRootViewAppearing(_ appearing: Bool) { isRootViewAppearingSubject.send(appearing) } }
ShowContentLogRootModifier
ShowContentLogRootModifierは、表示ログを送る「大元のView」に付与するViewModifierです。
このViewModifierは、
- ShowContentLogControllerのインスタンスをEnvironmentValuesに設定する
- ViewModiferが付けられた「大元のView」の表示状態をShowContentLogControllerに伝える
という2つの役割を担っています。
struct ShowContentLogRootModifier: ViewModifier { let controller: ShowContentLogController @State private var isAppearing: Bool = false func body(content: Content) -> some View { content .onAppear { isAppearing = true } .onDisappear { isAppearing = false } .onReceive(NotificationCenter.default.publisher(for: UIApplication.willEnterForegroundNotification)) { _ in if didEnterBackground { isAppearing = true didEnterBackground = false } } .onReceive(NotificationCenter.default.publisher(for: UIApplication.didEnterBackgroundNotification)) { _ in if isAppearing { isAppearing = false didEnterBackground = true } } .onChange(of: isAppearing) { appearing in controller.setIsRootViewAppearing(appearing) // 表示状態を ShowContentLogController のインスタンスに伝える } .environment(\.showContentLogController, controller) // EnvironmentValues に設定する }
PostShowContentLogModifier
PostShowContentLogModifierは、表示ログを送りたい各コンテンツのViewに付与するViewModifierです。
このViewModifierは、ShowContentLogControllerのisRootViewAppearing Publisherを監視しつつ、適切なタイミングで表示ログを送る役割を担っています。
また、ViewModifierが付与されたViewが現在表示されているか(isAppearing)、既に表示ログを送ったか(didPostLog)の状態をStateとして保持していて、監視しているisRootViewAppearingがfalseになった時(「大元のView」が非表示になった時)に、既に表示ログを送ったか(didPostLog)の状態をリセットしています。
* ShowContentLogControllerRequired(とAppEnvironmentRequired)については「実用段階にするまでに用意した仕組み」の章で詳しく説明します。
struct PostShowContentLogModifier<Category: LogCategory>: ViewModifier { let event: Category @State private var isRootViewAppearing: Bool = false @State private var isAppearing: Bool = false @State private var didPostLog: Bool = false func body(content: Content) -> some View { AppEnvironmentRequired { appEnvironment in ShowContentLogControllerRequired { showContentLogController in content .onAppear { isAppearing = true if isRootViewAppearing && !didPostLog { postLog(appEnvironment) } } .onDisappear { isAppearing = false } .onReceive(showContentLogController.isRootViewAppearing) { rootAppearing in if rootAppearing { isRootViewAppearing = true if isAppearing && !didPostLog { postLog(appEnvironment) } } else { isRootViewAppearing = false didPostLog = false // didPostLog の状態をリセット } } } } } private func postLog(_ appEnvironment: any AppEnvironment) { appEnvironment.activityLogger.post(event) didPostLog = true } }
設計時に検討したこと
ログを送ったかどうかの管理をどこで行うか
UIKit時代は、表示したコンテンツのIDをViewControllerのSetで管理し、親Viewが中央集権的に各コンテンツのログ送信フラグの管理を行っていました。しかし、SwiftUIでは全てのViewがIdentityを持っており、ログを送るView自身がStateでログを送ったかどうかを管理する方がSwiftUI的に自然だと考えました(加えて子Viewから親Viewに自身の Identifierを伝えて管理させるやりとりも減らすことができて、実装もシンプルになります)。そのためShowContentLogでは、PostShowContentLogModifierを付与したView自身がログ送信フラグの管理を行う設計となっています。
実用段階にするまでに用意した仕組み
ShowContentLogController
isPresented
対応するログの要件
- アプリがバックグラウンドからフォアグラウンドに復帰した時に、復帰時の画面に表示されているコンテンツの表示ログを送る
開発中に気付いたのですが、ShowContentLogを使っている画面上でモーダルを表示し、そのモーダルが表示されている状態でバックグラウンド→フォアグラウンド復帰した時に表示ログが送られていました。原因は、モーダルが表示されている状態でバックグラウンド→フォアグラウンド復帰した時にShowContentLogRootModifierのwillEnterForegroundNotification・didEnterBackgroundNotificationが発火していたことでした。
iOS版クックパッドアプリでは、モーダル表示を含めた画面遷移はUIKitで行われているため、ShowContentLogControllerの初期化時にSwiftUIのViewを表示しているViewControllerを渡して、モーダルを表示しているかどうかを取得するクロージャisPresented: () -> Boolを保持することにしました。
final class ShowContentLogController { ... let isPresented: () -> Bool init(screenViewController: UIViewController) { isPresented = { [weak screenViewController] in screenViewController?.presentedViewController != nil } } }
これをShowContentLogRootModifier内でdidEnterBackgroundNotificationの通知を受け取った時に参照することで、モーダルが表示されている状態でバックグラウンド→フォアグラウンド復帰した時には表示ログを送らないようにしています。
// ShowContentLogRootModifier .onReceive(NotificationCenter.default.publisher(for: UIApplication.willEnterForegroundNotification)) { _ in if didEnterBackground { isAppearing = true didEnterBackground = false } } .onReceive(NotificationCenter.default.publisher(for: UIApplication.didEnterBackgroundNotification)) { _ in // モーダルが表示されていない時だけ処理を行う if isAppearing && !controller.isPresented() { isAppearing = false didEnterBackground = true } }
willRefreshOnForeground
対応するログの要件
- 一定時間経過後の画面自動更新やPull to Refreshによる画面更新を行った時は、更新後の画面に表示されているコンテンツの表示ログを送る
- アプリがバックグラウンドからフォアグラウンドに復帰した時に、復帰時の画面に表示されているコンテンツの表示ログを送る
iOS版クックパッドアプリの一部の画面では、一定時間経過後に再びタブ切り替えで戻ってきたりバックグラウンド→フォアグラウンド復帰したりすると、画面の自動更新が行われます(自動更新の判定はViewControllerで行われています)。この時UIApplication.willEnterForegroundNotificationが送られるタイミングが自動更新が走るタイミングより早いので、バックグラウンド→フォアグラウンド復帰時に自動更新が走る場合は、更新前後で古いコンテンツの表示ログと更新後のコンテンツの表示ログが2回送られてしまっていました。
この場合は更新後の表示ログのみを送りたいので、ShowContentLogControllerに画面の更新が予定されているかどうかを取得するwillRefreshOnForeground: () -> Boolというクロージャを保持し、バックグラウンド→フォアグラウンド復帰時に画面の更新が予定されている場合は更新が終わるまでisAppearingの変更を待つようにしました。
final class ShowContentLogController { ... let willRefreshOnForeground: () -> Bool init(screenViewController: UIViewController, willRefreshOnForeground: @escaping () -> Bool = { false }) { isPresented = ... self.willRefreshOnForeground = willRefreshOnForeground } }
// ShowContentLogRootModifier .onReceive(NotificationCenter.default.publisher(for: UIApplication.willEnterForegroundNotification)) { _ in if didEnterBackground { // 画面をリフレッシュする場合はリフレッシュを待ってから isAppearing を true にする if !controller.willRefreshOnForeground() { isAppearing = true } didEnterBackground = false } } }
ShowContentLogRootModifier
forceDisappear
対応するログの要件
- タブの切り替えによって画面が再度表示された時に、その画面に表示されているコンテンツの表示ログを送る
forceDisappearをtrueにするとisAppearingの値を常にfalseにしてShowContentLogControllerに伝えることができます。
TabContentView(...) .showContentLogRoot( controller: tabState.showContentLogController, forceDisappear: selection != tabState.tabType // 違うタブが選択されている時は `isAppearing` の値を常に false にする )
// ShowContentLogRootModifier .onChange(of: forceDisappear) { newForceDisappear in controller.setIsRootViewAppearing(!newForceDisappear && isAppearing) } .onChange(of: isAppearing) { appearing in controller.setIsRootViewAppearing(!forceDisappear && appearing) }
元々はiOS14のTabViewで、選択されていないタブのonAppearが呼ばれることがあり、それを回避するために生まれました。それ以外にも、OSバージョン問わずタブの選択が完全に切り替わっていない時(スワイプで隣のタブが少しだけ見えている状態)にも隣のタブのonAppearが呼ばれていたので、iOS14のサポートを終了してからもこの指定は続けています。
ちなみにsetIsRootViewAppearing自体をスキップしてしまうと、各種イベントの発火タイミングによっては本来送られるべきログが送られなくなってしまう可能性があるため、このように値を上書きしてsetIsRootViewAppearingを呼ぶ方法を取っています。
isRefreshing
対応するログの要件
- 一定時間経過後の画面自動更新やPull to Refreshによる画面更新を行った時は、更新後の画面に表示されているコンテンツの表示ログを送る
更新時にdidPostLog(ログを送ったかどうか)をリセットするために用意されているpropertyです。
現在レシピサービス開発部でSwiftUIで新規画面を開発する時は、下記のScreenStateのようなものを使って画面の状態管理をしているので、このpropertyを使う必要はありません(画面更新時はScreenStateがloading→loadedとなりloadedに対応するViewが再生成されるため)。
enum ScreenState<T, E: Error> { case initial case loading(T?) case loaded(T) case error(E) }
例えば画面の表示切り替えをZStack内のViewのopacity変更で行っていて、画面更新時にViewが再生成されない場合にこのpropertyを使ってdidPostLogをリセットすることができます。
// ShowContentLogRootModifier var isRefreshing: Bool ... .onChange(of: isRefreshing) { refreshing in isAppearing = !refreshing }
PostShowContentLogModifier
ShowContentLogControllerRequired
ShowContentLogControllerRequiredは、PostShowContentLogModifierを付けたViewよりも上の階層でShowContentLogControllerのインスタンスがEnvironmentValuesに設定されていない(つまりShowContentLogRootModifierを付け忘れている)時にassertionFailureを起こすためのViewです。
import SwiftUI struct ShowContentLogControllerRequired<Content: View>: View { @Environment(\.showContentLogController) private var showContentLogController: ShowContentLogController? private let content: (ShowContentLogController) -> Content init(@ViewBuilder content: @escaping (_: ShowContentLogController) -> Content) { self.content = content } private func noEnvironment() -> some View { assertionFailure("You must pass the showContentLogController from a parent or ancestor view. If you use postShowContentLog modifier, add showContentLogRoot modifier to a parent or ancestor view.") return EmptyView() } var body: some View { if let showContentLogController = showContentLogController { content(showContentLogController) } else { noEnvironment() } } }
AppEnvironmentRequiredも同じような実装となっています(むしろShowContentLogControllerRequiredが先に実装されたAppEnvironmentRequiredの実装を参考にしています)。
AppEnvironmentRequiredがクロージャの引数に渡しているappEnvironmentは、iOS版クックパッド上で用意されている依存関係を取り出すためのDIコンテナで、PostShowContentLogModifier内ではappEnvironmentを用いて行動ログを送るための依存にアクセスしています。
appEnvironmentについては下記に詳しい説明があります(記事内ではEnvironmentと呼ばれています)。
https://techlife.cookpad.com/entry/2021/06/16/110000
onPostLog
onPostLog は「自動生成行動ログ」が送られるタイミングで呼び出されるクロージャで、「自動生成行動ログ」とは別のログを追加で送るためのものです。
// PostShowContentLogModifier private let onPostLog: ((any AppEnvironment) -> Void)? ... private func postLog(_ appEnvironment: any AppEnvironment) { appEnvironment.activityLogger.post(event) onPostLog?(appEnvironment) didPostLog = true }
完成版のコード
以下が、「実用段階にするまでに用意した仕組み」を踏まえた完成版のコードです。
*動作確認時の環境: Xcode 14.1、iOS Deployment Target 15.0
ShowContentLogController
import Combine import SwiftUI import UIKit @MainActor final class ShowContentLogController { private let isRootViewAppearingSubject = CurrentValueSubject<Bool, Never>(false) lazy var isRootViewAppearing: AnyPublisher<Bool, Never> = isRootViewAppearingSubject .removeDuplicates() .eraseToAnyPublisher() let isPresented: () -> Bool let willRefreshOnForeground: () -> Bool init(screenViewController: UIViewController, willRefreshOnForeground: @escaping () -> Bool = { false }) { isPresented = { [weak screenViewController] in screenViewController?.presentedViewController != nil } self.willRefreshOnForeground = willRefreshOnForeground } func setIsRootViewAppearing(_ appearing: Bool) { isRootViewAppearingSubject.send(appearing) } } private struct ShowContentLogControllerKey: EnvironmentKey { static let defaultValue: ShowContentLogController? = nil } extension EnvironmentValues { var showContentLogController: ShowContentLogController? { get { self[ShowContentLogControllerKey.self] } set { self[ShowContentLogControllerKey.self] = newValue } } }
ShowContentLogRootModifier
import SwiftUI private struct ShowContentLogRootModifier: ViewModifier { private let controller: ShowContentLogController private var isRefreshing: Bool private var forceDisappear: Bool @State private var isAppearing: Bool = false @State private var didEnterBackground: Bool = false init(controller: ShowContentLogController, isRefreshing: Bool, forceDisappear: Bool) { self.controller = controller self.isRefreshing = isRefreshing self.forceDisappear = forceDisappear } func body(content: Content) -> some View { content .onAppear { isAppearing = true } .onDisappear { isAppearing = false } .onReceive(NotificationCenter.default.publisher(for: UIApplication.willEnterForegroundNotification)) { _ in if didEnterBackground { // 画面をリフレッシュする場合はリフレッシュを待ってから isAppearing を true にする if !controller.willRefreshOnForeground() { isAppearing = true } didEnterBackground = false } } .onReceive(NotificationCenter.default.publisher(for: UIApplication.didEnterBackgroundNotification)) { _ in if isAppearing && !controller.isPresented() { isAppearing = false didEnterBackground = true } } .onChange(of: isRefreshing) { refreshing in isAppearing = !refreshing } .onChange(of: forceDisappear) { newForceDisappear in controller.setIsRootViewAppearing(!newForceDisappear && isAppearing) } .onChange(of: isAppearing) { appearing in controller.setIsRootViewAppearing(!forceDisappear && appearing) } .environment(\.showContentLogController, controller) } } extension View { func showContentLogRoot(controller: ShowContentLogController, isRefreshing: Bool = false, forceDisappear: Bool = false) -> some View { modifier(ShowContentLogRootModifier(controller: controller, isRefreshing: isRefreshing, forceDisappear: forceDisappear)) } }
PostShowContentLogModifier
import SwiftUI private struct PostShowContentLogModifier<Category: LogCategory>: ViewModifier { private let event: Category private let onPostLog: ((any AppEnvironment) -> Void)? @State private var isRootViewAppearing: Bool = false @State private var isAppearing: Bool = false @State private var didPostLog: Bool = false init(event: Category, onPostLog: ((any AppEnvironment) -> Void)?) { self.event = event self.onPostLog = onPostLog } func body(content: Content) -> some View { AppEnvironmentRequired { appEnvironment in ShowContentLogControllerRequired { showContentLogController in content .onAppear { isAppearing = true if isRootViewAppearing && !didPostLog { postLog(appEnvironment) } } .onDisappear { isAppearing = false } .onReceive(showContentLogController.isRootViewAppearing) { rootAppearing in if rootAppearing { isRootViewAppearing = true if isAppearing && !didPostLog { postLog(appEnvironment) } } else { isRootViewAppearing = false didPostLog = false } } } } } private func postLog(_ appEnvironment: any AppEnvironment) { appEnvironment.activityLogger.post(event) onPostLog?(appEnvironment) didPostLog = true } } extension View { func postShowContentLog<Category: LogCategory>(_ event: Category, onPostLog: ((any AppEnvironment) -> Void)? = nil) -> some View { modifier(PostShowContentLogModifier(event: event, onPostLog: onPostLog)) } }
まとめ
今回ご紹介したShowContentLogによって、SwiftUIの画面でもUIKit同様に各コンテンツの表示ログを送ることができるようになりました。また、UIKit時代は画面を作る度に一から表示ログの実装が必要だったのですが、仕組みを作ったことでSwiftUIでは表示ログを簡単に送ることができるようにもなりました。
仕組みを作る中で様々な意見・指摘をくれたチームの同僚に感謝します。この記事が、SwiftUIを使った画面で行動ログを送る際の参考に少しでもなれば幸いです。
*1:isRootViewAppearingを最初computed propertyにしていたのですが、それだとSwiftUIのViewのbodyが再実行される度にonReceiveで毎回新たなPublisherのインスタンスを購読するという挙動になりremoveDuplicatesが効かなくなってしまうので、lazy varで宣言しています。